Platycodonis Radix Alleviates LPS-Induced Lung Inflammation through Modulation of TRPA1 Channels
- PMID: 37446875
- PMCID: PMC10343319
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28135213
Platycodonis Radix Alleviates LPS-Induced Lung Inflammation through Modulation of TRPA1 Channels
Abstract
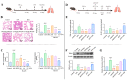
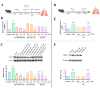
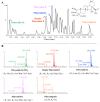
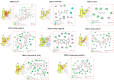
Platycodonis Radix (PR), a widely consumed herbal food, and its bioactive constituents, platycodins, have therapeutic potential for lung inflammation. Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin 1 (TRPA1), which is essential for the control of inflammation, may be involved in the development of inflammation in the lungs. The aim of this study was to determine the TRPA1-targeted effects of PR against pulmonary inflammation and to investigate the affinity of PR constituents for TRPA1 and their potential mechanisms of action. Using a C57BL/6J mouse lipopolysaccharides (LPS) intratracheal instillation pneumonia model and advanced analytical techniques (UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS, molecular docking, immuno-fluorescence), five platycodins were isolated from PR, and the interaction between these platycodins and hTRPA1 was verified. Additionally, we analyzed the impact of platycodins on LPS-induced TRPA1 expression and calcium influx in BEAS-2B cells. The results indicated that PR treatment significantly reduced the severity of LPS-triggered inflammation in the mouse model. Interestingly, there was a mild increase in the expression of TRPA1 caused by PR in healthy mice. Among five isolated platycodins identified in the PR extract, Platycodin D3 (PD3) showed the highest affinity for hTRPA1. The interaction between platycodins and TRPA1 was verified through molecular docking methods, highlighting the significance of the S5-S6 pore-forming loop in TRPA1 and the unique structural attributes of platycodins. Furthermore, PD3 significantly reduced LPS-induced TRPA1 expression and calcium ion influx in BEAS-2B cells, substantiating its own role as an effective TRPA1 modulator. In conclusion, PR and platycodins, especially PD3, show promise as potential lung inflammation therapeutics. Further research should explore the precise mechanisms by which platycodins modulate TRPA1 and their broader therapeutic potential.
Keywords: TRPA1; lung inflammation; platycodins; platycodonis radix.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Elucidating the anti-inflammatory activity of platycodins in lung inflammation through pulmonary distribution dynamics and grey relational analysis of cytokines.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Apr 6;323:117706. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.117706. Epub 2024 Jan 3. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38176670
-
Bioactive platycodins from Platycodonis Radix: Phytochemistry, pharmacological activities, toxicology and pharmacokinetics.Food Chem. 2020 Oct 15;327:127029. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127029. Epub 2020 May 19. Food Chem. 2020. PMID: 32450486 Review.
-
N-Acetyl-L-cysteine inhibits sulfur mustard-induced and TRPA1-dependent calcium influx.Arch Toxicol. 2017 May;91(5):2179-2189. doi: 10.1007/s00204-016-1873-x. Epub 2016 Oct 13. Arch Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 27738742
-
Complex Regulatory Role of the TRPA1 Receptor in Acute and Chronic Airway Inflammation Mouse Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 9;21(11):4109. doi: 10.3390/ijms21114109. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32526913 Free PMC article.
-
A role for transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 cation channel (TRPA1) in airway hyper-responsiveness?Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2015 Mar;93(3):171-6. doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2014-0417. Epub 2015 Jan 5. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25654580 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 by traditional Chinese medicine drugs and their active ingredients.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 6;16:1604765. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1604765. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40548057 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Memon T.A., Nguyen N.D., Burrell K.L., Scott A.F., Almestica-Roberts M., Rapp E., Deering-Rice C.E., Reilly C.A. Wood Smoke Particles Stimulate MUC5AC Overproduction by Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells through TRPA1 and EGFR Signaling. Toxicol. Sci. 2020;174:278–290. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfaa006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nummenmaa E., Hamalainen M., Pemmari A., Moilanen L.J., Tuure L., Nieminen R.M., Moilanen T., Vuolteenaho K., Moilanen E. Transient Receptor Potential Ankyrin 1 (TRPA1) Is Involved in Upregulating Interleukin-6 Expression in Osteoarthritic Chondrocyte Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021;22:87. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010087. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

