Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Immunoregulatory Activity of Rice Seed-Derived Peptide PEP1 on Dendritic Cells
- PMID: 37446885
- PMCID: PMC10343632
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28135224
Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Immunoregulatory Activity of Rice Seed-Derived Peptide PEP1 on Dendritic Cells
Abstract
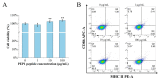
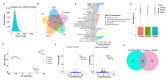
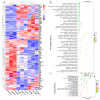
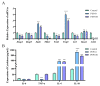
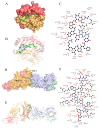
Some food-derived bioactive peptides exhibit prominent immunoregulatory activity. We previously demonstrated that the rice-derived PEP1 peptide, GIAASPFLQSAAFQLR, has strong immunological activity. However, the mechanism of this action is still unclear. In the present study, full-length transcripts of mouse dendritic cells (DC2.4) treated with PEP1 were sequenced using the PacBio sequencing platform, and the transcriptomes were compared via RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq). The characteristic markers of mature DCs, the cluster of differentiation CD86, and the major histocompatibility complex (MHC-II), were significantly upregulated after the PEP1 treatment. The molecular docking suggested that hydrogen bonding and electrostatic interactions played important roles in the binding between PEP1, MHC-II, and the T-cell receptor (TCR). In addition, the PEP1 peptide increased the release of anti-inflammatory factors (interleukin-4 and interleukin-10) and decreased the release of pro-inflammatory factors (interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α). Furthermore, the RNA-seq results showed the expression of genes involved in several signaling pathways, such as the NF-κB, MAPK, JAK-STAT, and TGF-β pathways, were regulated by the PEP1 treatment, and the changes confirmed the immunomodulatory effect of PEP1 on DC2.4 cells. This findings revealed that the PEP1 peptide, derived from the byproduct of rice processing, is a potential natural immunoregulatory alternative for the treatment of inflammation.
Keywords: dc2.4 cells; immunopeptide; immunoregulatory mechanism; rice-derived peptide; transcriptome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

