Hemostasis Strategies and Recent Advances in Nanomaterials for Hemostasis
- PMID: 37446923
- PMCID: PMC10343471
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28135264
Hemostasis Strategies and Recent Advances in Nanomaterials for Hemostasis
Abstract
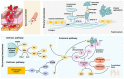
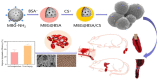
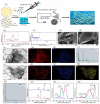
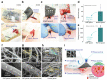
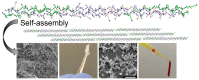
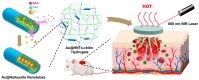
The development of materials that effectively stop bleeding and prevent wound adhesion is essential in both military and medical fields. However, traditional hemostasis methods, such as cautery, tourniquets, and gauze, have limitations. In recent years, new nanomaterials have gained popularity in medical and health fields due to their unique microstructural advantages. Compared to traditional materials, nanomaterials offer better adhesion, versatility, and improved bioavailability of traditional medicines. Nanomaterials also possess advantages such as a high degree and stability, self-degradation, fewer side effects, and improved wound healing, which make them ideal for the development of new hemostatic materials. Our review provides an overview of the currently used hemostatic strategies and materials, followed by a review of the cutting-edge nanomaterials for hemostasis, including nanoparticles and nanocomposite hydrogels. The paper also briefly describes the challenges faced by the application of nanomaterials for hemostasis and the prospects for their future development.
Keywords: effective hemostasis; hemostasis strategies; nanomaterials; nanotechnology; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Recent Advances in Hemostasis at the Nanoscale.Adv Healthc Mater. 2019 Dec;8(23):e1900823. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201900823. Epub 2019 Nov 7. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019. PMID: 31697456 Review.
-
Hemostatic nanotechnologies for external and internal hemorrhage management.Biomater Sci. 2020 Aug 21;8(16):4396-4412. doi: 10.1039/d0bm00781a. Epub 2020 Jul 13. Biomater Sci. 2020. PMID: 32658944 Review.
-
Research progress on MXenes in polysaccharide-based hemostasis and wound healing: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 Apr;303:140613. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.140613. Epub 2025 Feb 1. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 39900158 Review.
-
Recent advances in the application of clay-containing hydrogels for hemostasis and wound healing.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2024 Mar;21(3):457-477. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2024.2329641. Epub 2024 Mar 14. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2024. PMID: 38467560 Review.
-
Recent Advances in Topical Hemostatic Materials.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2024 Mar 18;7(3):1362-1380. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.3c01144. Epub 2024 Feb 19. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2024. PMID: 38373393 Review.
Cited by
-
Sono-responsive smart nanoliposomes for precise and rapid hemostasis application.RSC Adv. 2024 May 13;14(22):15491-15498. doi: 10.1039/d3ra08445k. eCollection 2024 May 10. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38741972 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of Hydrogels in Emergency Therapy.Gels. 2025 Mar 23;11(4):234. doi: 10.3390/gels11040234. Gels. 2025. PMID: 40277670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of Lavender Essential Oil on the Physical and Antibacterial Properties of Chitosan Sponge for Hemostatic Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 14;24(22):16312. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216312. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003499 Free PMC article.
-
Vanillic acid-based pro-coagulant hemostatic shape memory polymer foams with antimicrobial properties against drug-resistant bacteria.Acta Biomater. 2024 Nov;189:254-269. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2024.09.036. Epub 2024 Sep 27. Acta Biomater. 2024. PMID: 39343289
-
State of the art, trends, hotspots, and prospects of injection materials for controlling bleeding.Int Wound J. 2024 Jan;21(1):e14644. doi: 10.1111/iwj.14644. Int Wound J. 2024. PMID: 38272794 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

