Identification of Floral Volatile Components and Expression Analysis of Controlling Gene in Paeonia ostii 'Fengdan' under Different Cultivation Conditions
- PMID: 37447013
- PMCID: PMC10346646
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12132453
Identification of Floral Volatile Components and Expression Analysis of Controlling Gene in Paeonia ostii 'Fengdan' under Different Cultivation Conditions
Abstract
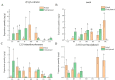
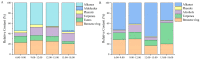
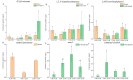
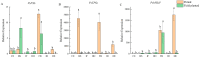
In order to explore the release rule of floral volatile substances and the diurnal variation of different flower development stages of Paeonia ostii 'Fengdan' in potted and ground-planted conditions, dynamic headspace adsorption combined with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry(GC-MS) was used to analyze the dynamic changes in floral volatile components and contents. Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was used to analyze changes in flower fragrance-regulating genes PsPAL, PsTPSs, and PsbHLH at different flower development stages and a daily change process at the full-blooming stage. The results show that there were differences in aroma components and contents of Paeonia ostii 'Fengdan' at different flower development stages and different time quantum of every day. There were 25 and 28 aroma components identified in 7 flower development stages of tree peonies planted in pots and in the field, respectively, and 23 and 22 aroma components identified at different time quantum of the day, of which the largest and highest content was alkanes. The main characteristic aroma substances were (E)-β-ocimene, 1,3,5-trimethoxybenzene, 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol, methyl jasmonate, nerol, and cinnamyl alcohol; released amounts of the abovementioned substances varied depending on the development stage and the time of the day. The expression of flower fragrance-controlling genes (PsPAL, PsTPSs, and PsbHLH) in tree peonies varied greatly in different conditions. The results of this study provide a valuable resource to investigate floral fragrance formation in tree peonies.
Keywords: Paeonia ostii; controlling gene; different cultivation conditions; floral volatile components.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no known competing financial interest or personal relationship that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
New insights on the analysis of phytosterols in pollen and anther wall of tree peony (Paeonia ostii 'Fengdan') revealed by GC-MS/MS.Anal Chim Acta. 2022 Jun 15;1212:339891. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2022.339891. Epub 2022 May 2. Anal Chim Acta. 2022. PMID: 35623781
-
Characteristics of PoVIN3, a Key Gene of Vernalization Pathway, Affects Flowering Time.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 13;23(22):14003. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214003. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430482 Free PMC article.
-
Dormancy-release, germination and seedling growth of Paeonia ostii 'Fengdan' seeds under measures of physical and chemical treatment and sowing.PLoS One. 2022 Jul 5;17(7):e0270767. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0270767. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35789330 Free PMC article.
-
RNA Sequencing Analysis and Verification of Paeonia ostii 'Fengdan' CuZn Superoxide Dismutase (PoSOD) Genes in Root Development.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jan 31;13(3):421. doi: 10.3390/plants13030421. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38337954 Free PMC article.
-
Flower morphology, flower color, flowering and floral fragrance in Paeonia L.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Nov 21;15:1467596. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1467596. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39640998 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diversity of Treatments in Overcoming Morphophysiological Dormancy of Paeonia peregrina Mill. Seeds.Plants (Basel). 2024 Aug 6;13(16):2178. doi: 10.3390/plants13162178. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39204614 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Characterization of Jasmonic Acid Methyltransferase Involved in the Formation of Floral Methyl Jasmonate in Hedychium coronarium.Plants (Basel). 2023 Dec 19;13(1):8. doi: 10.3390/plants13010008. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38202316 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang L., Guo D.L., Guo L.L., Guo Q., Wang H.F., Hou X.G. Construction of a high-density genetic map and QTLs 410 mapping with GBS from the interspecific F1 population of P. ostii ‘Fengdan Bai’ and P. suffruticosa ‘Xin Riyuejin’. Sci. Hortic. 2019;246:190–200. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2018.10.039. - DOI
-
- Luo X.N., Sun D.Y., Wang S., Luo S., Fu Y.Q., Niu L.X., Shi Q.Q., Zhang Y.L. Integrating full-length transcriptomics and metabolomics reveals the regulatory mechanisms underlying yellow pigmentation in tree peony (Paeonia suffruticosa Andr.) flowers. Hortic. Res. 2021;8:235. doi: 10.1038/s41438-021-00666-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Guo L.L., Li Y.Y., Lei Y., Gao J.S., Song C.W., Guo D.L., Hou X.G. Genome-scale investigation and identification of variations associated with early flowering based on whole genome resequencing and transcriptome integrated analysis in tree peony. Sci. Hortic. 2023;310:111695. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2022.111695. - DOI
-
- Li Y.Y., Guo L.L., Wang Z.Y., Zhao D.H., Guo D.L., Carlson J.E., Yin W.L., Hou X.G. Genome-wide association study of 23 flowering phenology traits and 4 floral agronomic traits in tree peony (Paeonia section Moutan DC.) reveals five genes known to regulate flowering time. Hortic. Res. 2023;10:uhac263. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhac263. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

