Assessment of Genetic Variability and Evolutionary Relationships of Rhizoctonia solani Inherent in Legume Crops
- PMID: 37447079
- PMCID: PMC10347096
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12132515
Assessment of Genetic Variability and Evolutionary Relationships of Rhizoctonia solani Inherent in Legume Crops
Abstract
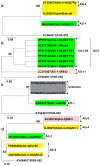
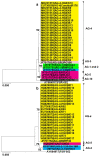
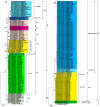
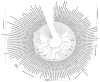
Rhizoctonia solani is one of the most common soil-borne fungal pathogens of legume crops worldwide. We collected rDNA-ITS sequences from NCBI GenBank, and the aim of this study was to examine the genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationships of various R. solani anastomosis groups (AGs) that are commonly associated with grain legumes (such as soybean, common bean, pea, peanut, cowpea, and chickpea) and forage legumes (including alfalfa and clover). Soybean is recognized as a host for multiple AGs, with AG-1 and AG-2 being extensively investigated. This is evidenced by the higher representation of sequences associated with these AGs in the NCBI GenBank. Other AGs documented in soybean include AG-4, AG-7, AG-11, AG-5, AG-6, and AG-9. Moreover, AG-4 has been extensively studied concerning its occurrence in chickpea, pea, peanut, and alfalfa. Research on the common bean has been primarily focused on AG-2, AG-4, and AG-1. Similarly, AG-1 has been the subject of extensive investigation in clover and cowpea. Collectively, AG-1, AG-2, and AG-4 have consistently been identified and studied across these diverse legume crops. The phylogenetic analysis of R. solani isolates across different legumes indicates that the distinct clades or subclades formed by the isolates correspond to their specific anastomosis groups (AGs) and subgroups, rather than being determined by their host legume crop. Additionally, there is a high degree of sequence similarity among isolates within the same clade or subclade. Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) further supports this finding, as isolates belonging to the same AGs and/or subgroups cluster together, irrespective of their host legume. Therefore, the observed clustering of R. solani AGs and subgroups without a direct association with the host legume crop provides additional support for the concept of AGs in understanding the genetic relationships and evolution of R. solani.
Keywords: Rhizoctonia solani; anastomosis groups; forage legumes; genetic diversity; grain legumes; phylogeny.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ogoshi A. Ecology and pathogenicity of anastomosis and intraspecific groups of Rhizoctonia solani Kuhn. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1987;25:125–143. doi: 10.1146/annurev.py.25.090187.001013. - DOI
-
- Sneh B. Non pathogenic isolates of Rhizoctonia spp.(np-R) and their role in biological control. In: Sneh B., Jabaji-Hare S., Neate S., Dijst G., editors. Rhizoctonia Species: Taxonomy, Molecular Biology, Ecology, Pathology and Disease Control. Kluwer Academic Publishers; Alphen aan den Rijn, The Netherlands: 1996. pp. 473–483.
-
- Ajayi-Oyetunde O., Bradley C. Rhizoctonia solani: Taxonomy, population biology and management of Rhizoctonia seedling disease of soybean. Plant Pathol. 2018;67:3–17. doi: 10.1111/ppa.12733. - DOI
-
- Zhang C., Yu S., Tian H., Wang Z., Yu B., Ma L., Nan Z., Fang X. Varieties with a high level of resistance provide an opportunity to manage root rot caused by Rhizoctonia solani in alfalfa. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2021;160:983–989. doi: 10.1007/s10658-021-02287-8. - DOI
-
- Jin D., Ma J., Ma W., Liang C., Shi Y., He J.-S. Legumes in Chinese Natural Grasslands: Species, Biomass, and Distribution. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2013;66:648–656. doi: 10.2111/REM-D-12-00159.1. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

