The Role of Anthocyanins in Plant Tolerance to Drought and Salt Stresses
- PMID: 37447119
- PMCID: PMC10346810
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12132558
The Role of Anthocyanins in Plant Tolerance to Drought and Salt Stresses
Abstract
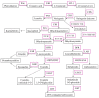
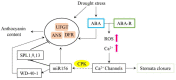
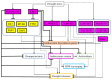
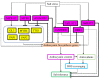
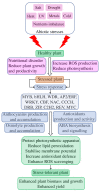
Drought and salinity affect various biochemical and physiological processes in plants, inhibit plant growth, and significantly reduce productivity. The anthocyanin biosynthesis system represents one of the plant stress-tolerance mechanisms, activated by surplus reactive oxygen species. Anthocyanins act as ROS scavengers, protecting plants from oxidative damage and enhancing their sustainability. In this review, we focus on molecular and biochemical mechanisms underlying the role of anthocyanins in acquired tolerance to drought and salt stresses. Also, we discuss the role of abscisic acid and the abscisic-acid-miRNA156 regulatory node in the regulation of drought-induced anthocyanin production. Additionally, we summarise the available knowledge on transcription factors involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis and development of salt and drought tolerance. Finally, we discuss recent progress in the application of modern gene manipulation technologies in the development of anthocyanin-enriched plants with enhanced tolerance to drought and salt stresses.
Keywords: abiotic stress; abscisic acid; anthocyanin; drought; microRNA; salinity stress; transcription factors (TFs).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Abiotic stress-induced anthocyanins in plants: Their role in tolerance to abiotic stresses.Physiol Plant. 2021 Jul;172(3):1711-1723. doi: 10.1111/ppl.13373. Epub 2021 Mar 1. Physiol Plant. 2021. PMID: 33605458 Review.
-
Evaluating the involvement and interaction of abscisic acid and miRNA156 in the induction of anthocyanin biosynthesis in drought-stressed plants.Planta. 2017 Aug;246(2):299-312. doi: 10.1007/s00425-017-2711-y. Epub 2017 May 22. Planta. 2017. PMID: 28534253 Review.
-
Environmental Stimuli and Phytohormones in Anthocyanin Biosynthesis: A Comprehensive Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 16;24(22):16415. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216415. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Constitutive expression of an A-5 subgroup member in the DREB transcription factor subfamily from Ammopiptanthus mongolicus enhanced abiotic stress tolerance and anthocyanin accumulation in transgenic Arabidopsis.PLoS One. 2019 Oct 23;14(10):e0224296. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0224296. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31644601 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the Sweet Potato MYB Transcription Factor IbMYB48 Confers Salt and Drought Tolerance in Arabidopsis.Genes (Basel). 2022 Oct 17;13(10):1883. doi: 10.3390/genes13101883. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36292768 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Unveiling the protective role of anthocyanin in rice: insights into drought-induced oxidative stress and metabolic regulation.Front Plant Sci. 2024 May 28;15:1397817. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1397817. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38863532 Free PMC article.
-
Cloned genes and genetic regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in maize, a comparative review.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Jan 24;15:1310634. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1310634. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38328707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcription factor ABF3 modulates salinity stress-enhanced jasmonate signaling in Arabidopsis.Plant Divers. 2024 May 18;46(6):791-803. doi: 10.1016/j.pld.2024.05.003. eCollection 2024 Nov. Plant Divers. 2024. PMID: 39811815 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated analysis of transcriptome, sRNAome, and degradome involved in the drought-response of maize Zhengdan958.Open Life Sci. 2025 Jan 27;20(1):20221044. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-1044. eCollection 2025. Open Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 39881824 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the differences in traits and genes between brown cotton and white cotton hybrid offspring (Gossypium hirsutum L.).Planta. 2025 Jan 14;261(2):35. doi: 10.1007/s00425-024-04601-0. Planta. 2025. PMID: 39810063
References
-
- Zhao X., Dai X., Gao L., Guo L., Zhuang J., Liu Y., Ma X., Wang R., Xia T., Wang Y. Functional Analysis of an Uridine Diphosphate Glycosyltransferase Involved in the Biosynthesis of Polyphenolic Glucoside in Tea Plants (Camellia sinensis) J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017;65:10993–11001. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b04969. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

