The Use of DAO as a Marker for Histamine Intolerance: Measurements and Determinants in a Large Random Population-Based Survey
- PMID: 37447214
- PMCID: PMC10346277
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15132887
The Use of DAO as a Marker for Histamine Intolerance: Measurements and Determinants in a Large Random Population-Based Survey
Abstract
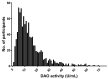
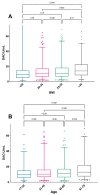
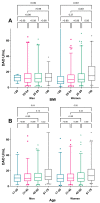
Histamine intolerance (HIT) is a common adverse reaction to food where elimination and reintroduction of histamine-rich food is part of the investigation. Analysis of the enzyme diamine oxidase (DAO) is sometimes used as an additional tool for diagnosis. This study aimed to describe the distribution of DAO in a large representative cohort of adults and to determine the association between DAO activity and possible associated factors. The study is based on the population-based West Sweden Asthma Study and includes 1051 subjects. Subjects underwent structured interviews including questions on demography, asthma, allergy symptoms, and lifestyle factors. Subjects were assessed for specific-IgE-antibodies and measurement of DAO activity in serum. Previously suggested cut-off levels for low values (<3 U/mL), normal values (>10 U/mL), and median levels of DAO were used. In the group of 1051 subjects, only a few presented reactions upon histamine intake, whereas 44% presented DAO levels below the suggested normal cut-off levels. BMI and age were shown to have an impact on DAO activity among women with increasing activity of DAO with increasing BMI and age. Among men, only increasing age was seen to have an impact on DAO levels. There was no difference in DAO levels with different sensitization status to common foods or airborne allergens. No association between DAO levels and reported symptoms to histamine-rich foods could be found. In conclusion, the determination of the DAO enzyme needs to be re-evaluated and may not be used as a valuable tool for histamine intolerance using current cut-off values. Further studies are needed to improve the use of DAO as a biomarker for histamine intolerance.
Keywords: IgE-mediated food allergy; diamine oxidase; food intolerance; histamine intolerance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Johansson S.G., Bieber T., Dahl R., Friedmann P.S., Lanier B.Q., Lockey R.F., Motala C., Ortega Martell J.A., Platts-Mills T.A., Ring J., et al. Revised nomenclature for allergy for global use: Report of the Nomenclature Review Committee of the World Allergy Organization, October 2003. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004;113:832–836. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2003.12.591. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Comas-Basté O., Latorre-Moratalla M.L., Bernacchia R., Veciana-Nogués M.T., Vidal-Carou M.C. New approach for the diagnosis of histamine intolerance based on the determination of histamine and methylhistamine in urine. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017;145:379–385. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2017.06.029. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

