Exploring the Role of 6G Technology in Enhancing Quality of Experience for m-Health Multimedia Applications: A Comprehensive Survey
- PMID: 37447735
- PMCID: PMC10347022
- DOI: 10.3390/s23135882
Exploring the Role of 6G Technology in Enhancing Quality of Experience for m-Health Multimedia Applications: A Comprehensive Survey
Abstract
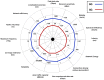
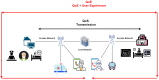
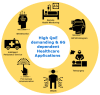
Mobile-health (m-health) is described as the application of medical sensors and mobile computing to the healthcare provision. While 5G networks can support a variety of m-health services, applications such as telesurgery, holographic communications, and augmented/virtual reality are already emphasizing their limitations. These limitations apply to both the Quality of Service (QoS) and the Quality of Experience (QoE). However, 6G mobile networks are predicted to proliferate over the next decade in order to solve these limitations, enabling high QoS and QoE. Currently, academia and industry are concentrating their efforts on the 6G network, which is expected to be the next major game-changer in the telecom industry and will significantly impact all other related verticals. The exponential growth of m-health multimedia traffic (e.g., audio, video, and images) creates additional challenges for service providers in delivering a suitable QoE to their customers. As QoS is insufficient to represent the expectations of m-health end-users, the QoE of the services is critical. In recent years, QoE has attracted considerable attention and has established itself as a critical component of network service and operation evaluation. This article aims to provide the first thorough survey on a promising research subject that exists at the intersection of two well-established domains, i.e., QoE and m-health, and is driven by the continuing efforts to define 6G. This survey, in particular, creates a link between these two seemingly distinct domains by identifying and discussing the role of 6G in m-health applications from a QoE viewpoint. We start by exploring the vital role of QoE in m-health multimedia transmission. Moreover, we examine how m-health and QoE have evolved over the cellular network's generations and then shed light on several critical 6G technologies that are projected to enable future m-health services and improve QoE, including reconfigurable intelligent surfaces, extended radio communications, terahertz communications, enormous ultra-reliable and low-latency communications, and blockchain. In contrast to earlier survey papers on the subject, we present an in-depth assessment of the functions of 6G in a variety of anticipated m-health applications via QoE. Multiple 6G-enabled m-health multimedia applications are reviewed, and various use cases are illustrated to demonstrate how 6G-enabled m-health applications are transforming human life. Finally, we discuss some of the intriguing research challenges associated with burgeoning multimedia m-health applications.
Keywords: 6G; e-health; healthcare; internet of things; m-health; multimedia; quality of experience.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Stefanova-Pavlova M., Andonov V., Tasseva V., Gateva A., Stefanova E. Imprecision and Uncertainty in Information Representation and Processing: New Tools Based on Intuitionistic Fuzzy Sets and Generalized Nets. Springer Publishing; Berlin, Germany: 2016. Generalized nets in medicine: An example of telemedicine for people with diabetes; pp. 327–357.
-
- Taleb H., Nasser A., Andrieux G., Charara N., Motta Cruz E. Wireless technologies, medical applications and future challenges in WBAN: A survey. Wirel. Netw. 2021;27:5271–5295. doi: 10.1007/s11276-021-02780-2. - DOI
-
- Smith-Bindman R., Miglioretti D.L., Johnson E., Lee C., Feigelson H.S., Flynn M., Greenlee R.T., Kruger R.L., Hornbrook M.C., Roblin D., et al. Use of diagnostic imaging studies and associated radiation exposure for patients enrolled in large integrated health care systems, 1996–2010. JAMA. 2012;307:2400–2409. doi: 10.1001/jama.2012.5960. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stefanova-Pavlova M., Andonov V., Stoyanov T., Angelova M., Cook G., Klein B., Vassilev P., Stefanova E. Recent Contributions in Intelligent Systems. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2017. Modeling telehealth services with generalized nets; pp. 279–290.
-
- Kashani M.H., Madanipour M., Nikravan M., Asghari P., Mahdipour E. A systematic review of IoT in healthcare: Applications, techniques, and trends. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2021;192:103164. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2021.103164. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

