Smart Farming Revolution: Portable and Real-Time Soil Nitrogen and Phosphorus Monitoring for Sustainable Agriculture
- PMID: 37447764
- PMCID: PMC10346605
- DOI: 10.3390/s23135914
Smart Farming Revolution: Portable and Real-Time Soil Nitrogen and Phosphorus Monitoring for Sustainable Agriculture
Abstract
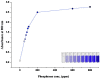
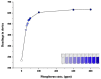
Precision agriculture is crucial for ensuring food security in a growing global population. Nutrients, their presence, concentration, and effectiveness, are key components in data-driven agriculture. Assessing macro and micro-nutrients, as well as factors such as water and pH, helps determine soil fertility, which is vital for supporting healthy plant growth and high crop yields. Insufficient soil nutrient assessment during continuous cropping can threaten long-term agricultural viability. Soil nutrients need to be measured and replenished after each harvest for optimal yield. However, existing soil testing procedures are expensive and time-consuming. The proposed research aims to assess soil nutrient levels, specifically nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations, to provide critical information and guidance on restoring optimal soil fertility. In this research, a novel chip-level colorimeter is fabricated to detect the N and P elements of soil onto a handheld colorimeter or spectrophotometer. Chemical reaction with soil solution generates color in the presence of nutrients, which are then quantitatively measured using sensors. The test samples are collected from various farmlands, and the results are validated with laboratory analysis of samples using spectrophotometers used in laboratories. ANOVA test has been performed in which F value > 1 in our study indicates statistically significant differences between the group means. The alternate hypothesis, which proposes the presence of significant differences between the groups, is supported by the data. The device created in this paper has crucial potential in terms of environmental and biological applications.
Keywords: Arduino Uno; IoT; LDR; LED; macro-nutrients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Amrutha A., Lekha R., Sreedevi A. Automatic soil nutrient detection and fertilizer dispensary system; Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Robotics: Current Trends and Future Challenges (RCTFC); Thanjavur, India. 19–20 December 2016; pp. 1–5.
-
- Baranwal T., Pateriya P.K. Development of IoT based smart security and monitoring devices for agriculture; Proceedings of the 2016 6th International Conference-Cloud System and Big Data Engineering (Confluence); Noida, India. 14–15 January 2016; pp. 597–602.
-
- Wong Y.J., Nakayama R., Shimizu Y., Kamiya A., Shen S., Rashid I.Z.M., Sulaiman N.M.N. Toward industrial revolution 4.0: Development, validation, and application of 3D-printed IoT-based water quality monitoring system. J. Clean. Prod. 2021;324:129230. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129230. - DOI
-
- Chanal P.M., Kakkasageri M.S. Security and privacy in IOT: A survey. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2020;115:1667–1693. doi: 10.1007/s11277-020-07649-9. - DOI
-
- Alyahya S., Khan W.U., Ahmed S., Marwat S.N.K., Habib S. Cyber secure framework for smart agriculture: Robust and tamper-resistant authentication scheme for IoT devices. Electronics. 2022;11:963. doi: 10.3390/electronics11060963. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

