Enhancement of Refractive Index Sensitivity Using Small Footprint S-Shaped Double-Spiral Resonators for Biosensing
- PMID: 37448026
- PMCID: PMC10346211
- DOI: 10.3390/s23136177
Enhancement of Refractive Index Sensitivity Using Small Footprint S-Shaped Double-Spiral Resonators for Biosensing
Abstract
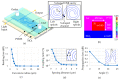
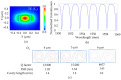
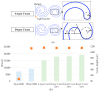
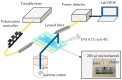
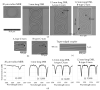
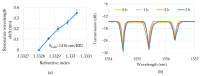
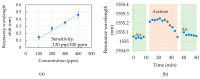
We demonstrate an S-shaped double-spiral microresonator (DSR) for detecting small volumes of analytes, such as liquids or gases, penetrating a microfluidic channel. Optical-ring resonators have been applied as label-free and high-sensitivity biosensors by using an evanescent field for sensing the refractive index of analytes. Enlarging the ring resonator size is a solution for amplifying the interactions between the evanescent field and biomolecules to obtain a higher refractive index sensitivity of the attached analytes. However, it requires a large platform of a hundred square millimeters, and 99% of the cavity area would not involve evanescent field sensing. In this report, we demonstrate the novel design of a Si-based S-shaped double-spiral resonator on a silicon-on-insulator substrate for which the cavity size was 41.6 µm × 88.4 µm. The proposed resonator footprint was reduced by 680 times compared to a microring resonator with the same cavity area. The fabricated resonator exposed more sensitive optical characteristics for refractive index biosensing thanks to the enhanced contact interface by a long cavity length of DSR structures. High quality factors of 1.8 × 104 were demonstrated for 1.2 mm length DSR structures, which were more than two times higher than the quality factors of microring resonators. A bulk sensitivity of 1410 nm/RIU was calculated for detecting 1 µL IPA solutions inside a 200 µm wide microchannel by using the DSR cavity, which had more than a 10-fold higher sensitivity than the sensitivity of the microring resonators. A DSR device was also used for the detection of 100 ppm acetone gas inside a closed bottle.
Keywords: cavity length; evanescent field sensing; refractive index; ring resonator.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Washburn A.L., Luchansky M.S., McClellan M.S., Bailey R.C. Label-free, multiplexed biomolecular analysis using arrays of silicon photonic microring resonators. Procedia Eng. 2011;25:63–66. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2011.12.016. - DOI
-
- Park M.K., Yiying J.Q., Kee J.S., Song J., Kao L.T.H., Fang Q., Guo-Qiang L., Netto V., Fosse E.M.L. Silicon micro-ring resonators for label-free aptamer-based biosensing; Proceedings of the 2012 7th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA); Singapore. 18–20 July 2012; pp. 1599–1602. - DOI
-
- Luan E., Yun H., Laplatine L., Dattner Y., Ratner D.M., Cheung K.C., Chrostowski L. Enhanced Sensitivity of Subwavelength Multibox Waveguide Microring Resonator Label-Free Biosensors. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2019;25:1–11. doi: 10.1109/JSTQE.2018.2821842. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

