Demarcating Z-line and Gastric Folds Boundary Based on the Segmentation of the Lower Esophageal Sphincter Images
- PMID: 37448539
- PMCID: PMC10336909
- DOI: 10.4103/jmss.jmss_182_21
Demarcating Z-line and Gastric Folds Boundary Based on the Segmentation of the Lower Esophageal Sphincter Images
Abstract
Background and objective: The endoscopic diagnosis of pathological changes in the gastroesophageal junction including esophagitis and Barrett's mucosa is based on the visual detection of two boundaries: mucosal color change between esophagus and stomach, and top endpoint of gastric folds. The presence and pattern of mucosal breaks in the gastroesophageal mucosal junction (Z line) classify esophagitis in patients and the distance between the two boundaries points to the possible columnar lined epithelium. Since visual detection may suffer from intra- and interobserver variability, our objective was to define the boundaries automatically based on image processing algorithms, which may enable us to measure the detentions of changes in future studies.
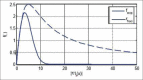
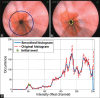
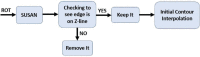
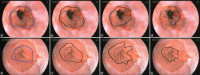
Methods: To demarcate the Z-line, first the artifacts of endoscopy images are eliminated. In the second step, using SUSAN edge detector, Mahalanobis distance criteria, and Gabor filter bank, an initial contour is estimated for the Z-line. Using region-based active contours, this initial contour converges to the Z-line. Finally, by applying morphological operators and Gabor Filter Bank to the region inside of the Z-line, gastric folds are segmented.
Results: To evaluate the results, a database consisting of 50 images and their ground truths were collected. The average dice coefficient and mean square error of Z-line segmentation were 0.93 and 3.3, respectively. Furthermore, the average boundary distance criteria are 12.3 pixels. In addition, two other criteria that compare the segmentation of folds with several ground truths, i.e., Sweet-Spot Coverage and Jaccard Index for Golden Standard, are 0.90 and 0.84, respectively.
Conclusions: Considering the results, automatic segmentation of Z-line and gastric folds are matched to the ground truths with appropriate accuracy.
Keywords: Adenocarcinoma; Barrett's esophagus; demarcating Z-line and gastric folds boundary; segmentation of lower esophageal sphincter endoscopy images.
Copyright: © 2023 Journal of Medical Signals & Sensors.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures













References
-
- Nasseri-Moghaddam S, Razjouyan H, Nouraei M, Alimohammadi M, Mamarabadi M, Va-Hedi H, et al. Inter-and intra-observer variability of the los angeles classification: A reassessment. Arch Iran Med. 2007;10:48–53. - PubMed
-
- Spechler SJ. Barrett's esophagus. Principles of Deglutition. :723–738.
-
- Armstrong, David, et al. The endoscopic assessment of esophagitis: a progress report on observer agreement. Gastroenterology 111.1. 1996:85–92. - PubMed
-
- Sharma P, Dent J, Armstrong D, Bergman JJ, Gossner L, Hoshihara Y, et al. The development and validation of an endoscopic grading system for barretts esophagus: The prague C & M criteria. Gastroenterology. 2006;131:1392–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
