Fluorescent nanodiamonds as innovative delivery systems for MiR-34a replacement in breast cancer
- PMID: 37449042
- PMCID: PMC10336355
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2023.06.012
Fluorescent nanodiamonds as innovative delivery systems for MiR-34a replacement in breast cancer
Abstract
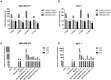
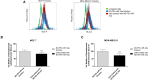
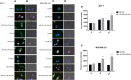
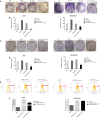
Nanodiamonds are innovative nanocrystalline carbon particles able to deliver chemically conjugated miRNAs. In oncology, the use of miRNA-based therapies may represent an advantage, based on their ability to simultaneously target multiple intracellular oncogenic targets. Here, nanodiamonds were tested and optimized to deliver miR-34a, a miRNA playing a key role in inhibiting tumor development and progression in many cancers. The physical-chemical properties of nanodiamonds were investigated suggesting electrical stability and uniformity of structure and size. Moreover, we evaluated nanodiamond cytotoxicity on two breast cancer cell models and confirmed their excellent biocompatibility. Subsequently, nanodiamonds were conjugated with miR-34a, using the chemical crosslinker polyethyleneimine; real-time PCR analysis revealed a higher level of miR-34a in cancer cells treated with the different formulations of nanodiamonds than with commercial transfectant. A significant and early nanodiamond-miR-34a uptake was recorded by FACS and fluorescence microscopy analysis in MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 cells. Moreover, nanodiamond-miR-34a significantly inhibited both cell proliferation and migration. Finally, a remarkable anti-tumor effect of miR-34a-conjugated nanodiamonds was observed in both heterotopic and orthotopic murine xenograft models. In conclusion, this study provides a rationale for the development of new therapeutic strategies based on use of miR-34a delivered by nanodiamonds to improve the clinical treatment of neoplasms.
Keywords: MT: Delivery Strategies; MiR-34a; MicroRNA; breast cancer; gene delivery; gene therapy; miRNA replacement therapy; nanodiamonds; nanomedicine; nanotechnology.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The all authors declare that they have no conflicts of interests.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

