Stereoselective alkyl C-glycosylation of glycosyl esters via anomeric C-O bond homolysis: efficient access to C-glycosyl amino acids and C-glycosyl peptides
- PMID: 37449071
- PMCID: PMC10337754
- DOI: 10.1039/d3sc01995k
Stereoselective alkyl C-glycosylation of glycosyl esters via anomeric C-O bond homolysis: efficient access to C-glycosyl amino acids and C-glycosyl peptides
Abstract
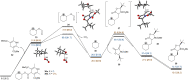
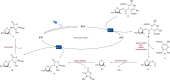
C-Glycosyl peptides possess excellent metabolic stability and therapeutic properties and thus play critical roles in biological studies as well as drug discoveries. However, the limited accessibility of C-glycosyl amino acids has significantly hindered the broader research of their structural features and mode of action. Herein, for the first time we disclose a novel visible-light-driven radical conjugate addition of 1,4-dihydropyridine (DHP)-derived glycosyl esters with dehydroalanine derivatives, generating C-glycosyl amino acids and C-glycosyl peptides in good yields with excellent stereoselectivities. Redox-active glycosyl esters, as readily accessible and bench-stable radical precursors, could be easily converted to glycosyl radicals via anomeric C(sp3)-O bond homolysis under mild conditions. Importantly, the generality and practicality of this transformation were fully demonstrated in >40 examples including 2-dexosugars, oligosaccharides, oligopeptides, and complex drug molecules. Given its mild reaction conditions, robust sugar scope, and high anomeric control and diastereoselectivity, the method presented herein could find widespread utility in the preparation of C(sp3)-linked sugar-based peptidomimetics.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
A patent application by S. Z., L.-G. X., F. Z., A. C., and Y. H. detailing part of this research was filed through the Patent Office of the People's Republic of China (November 2022). S. Z., L.-G. X., F. Z., A. C., and Y. H. declare no other competing interests. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

