Modulation of IL-17 backbone dynamics reduces receptor affinity and reveals a new inhibitory mechanism
- PMID: 37449080
- PMCID: PMC10337760
- DOI: 10.1039/d3sc00728f
Modulation of IL-17 backbone dynamics reduces receptor affinity and reveals a new inhibitory mechanism
Abstract
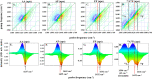
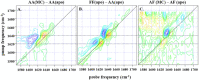
Knowledge of protein dynamics is fundamental to the understanding of biological processes, with NMR and 2D-IR spectroscopy being two of the principal methods for studying protein dynamics. Here, we combine these two methods to gain a new understanding of the complex mechanism of a cytokine:receptor interaction. The dynamic nature of many cytokines is now being recognised as a key property in the signalling mechanism. Interleukin-17s (IL-17) are proinflammatory cytokines which, if unregulated, are associated with serious autoimmune diseases such as psoriasis, and although there are several therapeutics on the market for these conditions, small molecule therapeutics remain elusive. Previous studies, exploiting crystallographic methods alone, have been unable to explain the dramatic differences in affinity observed between IL-17 dimers and their receptors, suggesting there are factors that cannot be fully explained by the analysis of static structures alone. Here, we show that the IL-17 family of cytokines have varying degrees of flexibility which directly correlates to their receptor affinities. Small molecule inhibitors of the cytokine:receptor interaction are usually thought to function by either causing steric clashes or structural changes. However, our results, supported by other biophysical methods, provide evidence for an alternate mechanism of inhibition, in which the small molecule rigidifies the protein, causing a reduction in receptor affinity. The results presented here indicate an induced fit model of cytokine:receptor binding, with the more flexible cytokines having a higher affinity. Our approach could be applied to other systems where the inhibition of a protein-protein interaction has proved intractable, for example due to the flat, featureless nature of the interface. Targeting allosteric sites which modulate protein dynamics, opens up new avenues for novel therapeutic development.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Daniel J. Shaw, Monika-Sarah E. D. Schulze, Christine E. Prosser, Alastair D. G. Lawson, Alistair J. Henry and Richard J. Taylor are or have been employees of UCB and may hold UCB shares and/or stock options.
Figures



References
-
- Krueger J. G. Wharton, Jr K. A. Schlitt T. Suprun M. Torene R. I. Jiang X. Wang C. Q. Fuentes-Duculan J. Hartmann N. Peters T. Koroleva I. Hillenbrand R. Letzkus M. Yu X. Li Y. Glueck A. Hasselberg A. Flannery B. Suarez-Farinas M. Hueber W. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019;144:750–763. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2019.04.029. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Reich K. Papp K. A. Matheson R. T. Tu J. H. Bissonnette R. Bourcier M. Gratton D. Kunynetz R. A. Poulin Y. Rosoph L. A. Stingl G. Bauer W. M. Salter J. M. Falk T. M. Blodorn-Schlicht N. A. Hueber W. Sommer U. Schumacher M. M. Peters T. Kriehuber E. Lee D. M. Wieczorek G. A. Kolbinger F. Bleul C. C. Exp. Dermatol. 2015;24:529–535. doi: 10.1111/exd.12710. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

