Hybrid sequencing discloses unique aspects of the transcriptomic architecture in equid alphaherpesvirus 1
- PMID: 37449092
- PMCID: PMC10336594
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17716
Hybrid sequencing discloses unique aspects of the transcriptomic architecture in equid alphaherpesvirus 1
Abstract
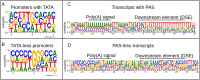
This study employed both short-read sequencing (SRS, Illumina) and long-read sequencing (LRS Oxford Nanopore Technologies) platforms to conduct a comprehensive analysis of the equid alphaherpesvirus 1 (EHV-1) transcriptome. The study involved the annotation of canonical mRNAs and their transcript variants, encompassing transcription start site (TSS) and transcription end site (TES) isoforms, in addition to alternative splicing forms. Furthermore, the study revealed the presence of numerous non-coding RNA (ncRNA) molecules, including intergenic and antisense transcripts, produced by EHV-1. An intriguing finding was the abundant production of chimeric transcripts, some of which potentially encode fusion polypeptides. Moreover, EHV-1 exhibited a greater incidence of transcriptional overlaps and splicing compared to related viruses. It is noteworthy that many genes have their unique TESs along with the co-terminal transcription ends, a characteristic scarcely seen in other alphaherpesviruses. The study also identified transcripts that overlap the replication origins of the virus. Moreover, a novel ncRNA, referred to as NOIR, was found to intersect with the 5'-ends of longer transcript isoform specified by the major transactivator genes ORF64 and ORF65, surrounding the OriL. These findings together imply the existence of a key regulatory mechanism that governs both transcription and replication through, among others, a process that involves interference between the DNA and RNA synthesis machineries.
Keywords: Direct RNA sequencing; EHV-1; Equid alphaherpesvirus 1; Illumina sequencing; Long-read sequencing; Nanopore sequencing; Replication origin; Transcriptome.
© 2023 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Mapping the temporal transcriptomic signature of a viral pathogen through CAGE and nanopore sequencing.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 15;20(4):e0320439. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320439. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40233049 Free PMC article.
-
Long-read sequencing uncovers a complex transcriptome topology in varicella zoster virus.BMC Genomics. 2018 Dec 4;19(1):873. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-5267-8. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 30514211 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Long-Read Sequencing Survey of Herpes Simplex Virus Dynamic Transcriptome.Front Genet. 2019 Sep 24;10:834. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00834. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31608102 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Read Sequencing - A Powerful Tool in Viral Transcriptome Research.Trends Microbiol. 2019 Jul;27(7):578-592. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2019.01.010. Epub 2019 Feb 26. Trends Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30824172 Review.
-
Long-Read Sequencing Revealed an Extensive Transcript Complexity in Herpesviruses.Front Genet. 2018 Jul 17;9:259. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00259. eCollection 2018. Front Genet. 2018. PMID: 30065753 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A functional interleukin-4 homolog is encoded in the genome of infectious laryngotracheitis virus: Unveiling a novel virulence factor.PLoS Pathog. 2025 Jul 23;21(7):e1013219. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1013219. eCollection 2025 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2025. PMID: 40700459 Free PMC article.
-
Long-read Transcriptomics of Caviid Gammaherpesvirus 1: Compiling a Comprehensive RNA Atlas.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 13:2024.12.11.627975. doi: 10.1101/2024.12.11.627975. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: mSystems. 2025 Mar 18;10(3):e0167824. doi: 10.1128/msystems.01678-24. PMID: 39713410 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Temporal transcriptional profiling of host cells infected by a veterinary alphaherpesvirus using nanopore sequencing.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 25;15(1):3247. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-87536-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39863683 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping the temporal transcriptomic signature of a viral pathogen through CAGE and nanopore sequencing.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 15;20(4):e0320439. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320439. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40233049 Free PMC article.
-
Long-read transcriptomics of caviid gammaherpesvirus 1: compiling a comprehensive RNA atlas.mSystems. 2025 Mar 18;10(3):e0167824. doi: 10.1128/msystems.01678-24. Epub 2025 Feb 27. mSystems. 2025. PMID: 40013795 Free PMC article.
References
-
- O’Callaghan DJ H.R. Academic Press, Harcourt Brace & Company; San Diego, CA: 1994. Encyclopedia of Virology.
-
- Allen G.P., Bryans J.T. Molecular epizootiology, pathogenesis, and prophylaxis of equine herpesvirus-1 infections. Prog. Vet. Microbiol. Immunol. 1986;2:78–144. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2856183 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

