Gut-microbiome-brain axis: the crosstalk between the vagus nerve, alpha-synuclein and the brain in Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 37449597
- PMCID: PMC10358673
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.373673
Gut-microbiome-brain axis: the crosstalk between the vagus nerve, alpha-synuclein and the brain in Parkinson's disease
Abstract
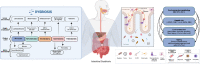
This critical review of the literature shows that there is a close link between the microbiome, the gut, and the brain in Parkinson's disease. The vagus nerve, the main component of the parasympathetic nervous system, is involved in the regulation of immune response, digestion, heart rate, and control of mood. It can detect microbiota metabolites through its afferents, transferring this gut information to the central nervous system. Preclinical and clinical studies have shown the important role played by the gut microbiome and gut-related factors in disease development and progression, as well as treatment responses. These findings suggest that the gut microbiome may be a valuable target for new therapeutic strategies for Parkinson's disease. More studies are needed to better understand the underlying biology and how this axis can be modulated for the patient's benefit.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; alpha-synuclein; enteric microbiota; gastrointestinal tract; vagus nerve.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
References
-
- Abdel-Haq R, Schlachetzki JCM, Boktor JC, Cantu-Jungles TM, Thron T, Zhang M, Bostick JW, Khazaei T, Chilakala S, Morais LH, Humphrey G, Keshavarzian A, Katz JE, Thomson M, Knight R, Gradinaru V, Hamaker BR, Glass CK, Mazmanian SK. A prebiotic diet modulates microglial states and motor deficits in α-synuclein overexpressing mice. Elife. 2022;11:e81453. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alipour Nosrani E, Tamtaji OR, Alibolandi Z, Sarkar P, Ghazanfari M, Azami Tameh A, Taghizadeh M, Banikazemi Z, Hadavi R, Naderi Taheri M. Neuroprotective effects of probiotics bacteria on animal model of Parkinson's disease induced by 6-hydroxydopamine:A behavioral, biochemical, and histological study. J Immunoassay Immunochem. 2021;42:106–120. - PubMed
-
- Arneth BM. Gut–brain axis biochemical signalling from the gastrointestinal tract to the central nervous system:gut dysbiosis and altered brain function. Postgrad Med J. 2018;94:446–452. - PubMed
-
- Baizabal-Carvallo JF, Alonso-Juarez M. The link between gut dysbiosis and neuroinflammation in Parkinson's disease. Neuroscience. 2020;432:160–173. - PubMed
-
- Beach TG, Adler CH, Sue LI, Shill HA, Driver-Dunckley E, Mehta SH, Intorcia AJ, Glass MJ, Walker JE, Arce R, Nelson CM, Serrano GE. Vagus nerve and stomach synucleinopathy in Parkinson's disease, incidental Lewy body disease, and normal elderly subjects:evidence against the “Body-First”Hypothesis. J Parkinsons Dis. 2021;11:1833–1843. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

