Waterpipe smoke inhalation induces lung injury and aortic endothelial dysfunction in mice
- PMID: 37449747
- PMCID: PMC10669000
- DOI: 10.33549/physiolres.935042
Waterpipe smoke inhalation induces lung injury and aortic endothelial dysfunction in mice
Abstract
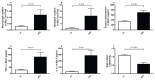
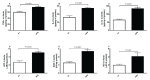
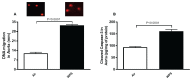
Waterpipe tobacco smoking (WPS) inhalation has been shown to trigger endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis. However, the mechanisms underlying these effects are still unknown. Here, we assessed the impact and underlying mechanism of WPS exposure for one month on endothelial dysfunction using aortic tissue of mice. The duration of the session was 30 min/day and 5 days/week. Control mice were exposed to air. Inhalation of WPS induced an increase in the number of macrophages and neutrophils and the concentrations of protein, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha), interleukin (IL)-1beta, and glutathione in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. Moreover, the concentrations of proinflammatory cytokines (TNF alpha, IL-6 and IL-1beta), adhesion molecules (intercellular adhesion molecule-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, E-selectin and P-selectin) and markers of oxidative stress (lipid peroxidation, glutathione, superoxide dismutase and nitric oxide) in aortic homogenates of mice exposed to WPS were significantly augmented compared with air exposed mice. Likewise, the concentration of galectin-3 was significantly increased in the aortic homogenates of mice exposed to WPS compared with control group. WPS inhalation induced vascular DNA damage assessed by comet assay and apoptosis characterized by a significant increase in cleaved caspase-3. While the aortic expression of phosphorylated nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) was significantly increased following WPS inhalation, the concentration of sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) was significantly decreased in WPS group compared with air-exposed group. In conclusion, our study provided evidence that WPS inhalation triggers lung injury and endothelial inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis which were associated with nuclear factor-kappaB activation and SIRT1 down-regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
