Psychometric Analysis of the Modified Differential Emotions Scale and the Six-Item Life Orientation Test-Revised in a Cohort of Older Women from the Women's Health Initiative
- PMID: 37449819
- PMCID: PMC10510696
- DOI: 10.1089/jwh.2023.0056
Psychometric Analysis of the Modified Differential Emotions Scale and the Six-Item Life Orientation Test-Revised in a Cohort of Older Women from the Women's Health Initiative
Abstract
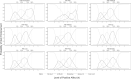
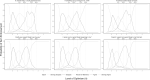
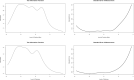
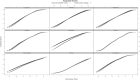
Background: Positive affect and emotional resources, such as optimism, may play a major role in women's health and promote healthy well-being later in life. However, positive affect and optimism measures have not been psychometrically assessed in older women, despite relations to health. Therefore, the objective of this study was to psychometrically assess measures of positive affect and optimism and test their association with other measures of well-being. Methods: In a Women's Health Initiative subcohort of 58,810 women (mean age [standard deviation] 79.0 [6.1]; 89% White), positive affect and optimism were measured using the modified Differential Emotions Scale (mDES) and Life Orientation Test-Revised (LOT-R), respectively. Reliability was tested using Cronbach's alpha and McDonald's omega. Performance was assessed using item response theory. Factor analysis was used to explore the construct validity of the LOT-R. Convergent and divergent validity with other well-being measures was tested. Results: Results suggest good reliability (mDES: Cronbach's alpha = 0.90 and omega total = 0.92; LOT-R: Cronbach's alpha = 0.79, omega hierarchical = 0.61, and omega total = 0.83). Item response analyses indicate mDES's ability to discriminate across positive affect; LOT-R was skewed toward lower optimism levels. Exploratory factor analyses suggest a two-factor solution for the LOT-R. Significant, but small correlations in expected directions to well-being measures confirmed validity hypotheses. Conclusions: The mDES and LOT-R measured positive affect and optimism with good reliability, item performance, and validity in a large sample of older postmenopausal women, supporting use of these measures to quantify effects of positive affect and optimism-promoting interventions.
Keywords: mental health; optimism; positive affect; postmenopausal women; psychometrics.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Health-related quality of life scale specific to pregnant women (PregQOL): Development and psychometric evaluation.Midwifery. 2025 Apr;143:104329. doi: 10.1016/j.midw.2025.104329. Epub 2025 Feb 6. Midwifery. 2025. PMID: 39923293
-
Psychometric properties of the Chinese version of the Menopause-Specific Quality-of-Life questionnaire.Menopause. 2017 May;24(5):546-554. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000000784. Menopause. 2017. PMID: 27922934 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of the female sexual distress scale-revised for assessing distress in women with hypoactive sexual desire disorder.J Sex Med. 2008 Feb;5(2):357-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2007.00672.x. Epub 2007 Nov 27. J Sex Med. 2008. PMID: 18042215
-
Reliability and validity of the Women's Health Initiative Insomnia Rating Scale.Psychol Assess. 2003 Jun;15(2):137-48. doi: 10.1037/1040-3590.15.2.137. Psychol Assess. 2003. PMID: 12847774
-
The General Hopelessness Scale: Development of a measure of hopelessness for non-clinical samples.PLoS One. 2023 Jun 26;18(6):e0287016. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0287016. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37363918 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Medina LD, Sabo S, Vespa J. Living Longer: Historical and Projected Life Expectancy in the United States, 1960 to 2060. Population Estimates and Projections. Current Population Reports; 2020. Available from: https://www.census.gov/content/dam/Census/library/publications/2020/demo... [Last accessed: April 15, 2022].
-
- Fredrickson BL. Positive Emotions Broaden and Build. In: Advances in Experimental Social Psychology, Volume 47. (Devine P, Plant A. eds.) Academic Press; 2013; pp. 1–53; doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-407236-7.00001-2 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

