γ-Secretase fanning the fire of innate immunity
- PMID: 37449907
- PMCID: PMC11212119
- DOI: 10.1042/BST20221445
γ-Secretase fanning the fire of innate immunity
Abstract
Innate immunity is the first line of defense against pathogens, alerting the individual cell and surrounding area to respond to this potential invasion. γ-secretase is a transmembrane protease complex that plays an intricate role in nearly every stage of this innate immune response. Through regulation of pattern recognition receptors (PRR) such as TREM2 and RAGE γ-secretase can modulate pathogen recognition. γ-secretase can act on cytokine receptors such as IFNαR2 and CSF1R to dampen their signaling capacity. While γ-secretase-mediated regulated intramembrane proteolysis (RIP) can further moderate innate immune responses through downstream signaling pathways. Furthermore, γ-secretase has also been shown to be regulated by the innate immune system through cytokine signaling and γ-secretase modulatory proteins such as IFITM3 and Hif-1α. This review article gives an overview of how γ-secretase is implicated in innate immunity and the maintenance of its responses through potentially positive and negative feedback loops.
Keywords: Hif1a; IFITM3; cytokine signaling; inflammation; innate immunity; regulated intramembrane proteolysis.
© 2023 The Author(s). Published by Portland Press Limited on behalf of the Biochemical Society.
Figures
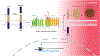

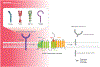
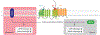
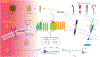
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

