Succinate mediates inflammation-induced adrenocortical dysfunction
- PMID: 37449973
- PMCID: PMC10374281
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.83064
Succinate mediates inflammation-induced adrenocortical dysfunction
Abstract
The hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis is activated in response to inflammation leading to increased production of anti-inflammatory glucocorticoids by the adrenal cortex, thereby representing an endogenous feedback loop. However, severe inflammation reduces the responsiveness of the adrenal gland to adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), although the underlying mechanisms are poorly understood. Here, we show by transcriptomic, proteomic, and metabolomic analyses that LPS-induced systemic inflammation triggers profound metabolic changes in steroidogenic adrenocortical cells, including downregulation of the TCA cycle and oxidative phosphorylation, in mice. Inflammation disrupts the TCA cycle at the level of succinate dehydrogenase (SDH), leading to succinate accumulation and disturbed steroidogenesis. Mechanistically, IL-1β reduces SDHB expression through upregulation of DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) and methylation of the SDHB promoter. Consequently, increased succinate levels impair oxidative phosphorylation and ATP synthesis and enhance ROS production, leading to reduced steroidogenesis. Together, we demonstrate that the IL-1β-DNMT1-SDHB-succinate axis disrupts steroidogenesis. Our findings not only provide a mechanistic explanation for adrenal dysfunction in severe inflammation, but also offer a potential target for therapeutic intervention.
Keywords: DNMT1; IL-1β; adrenal gland; cell biology; glucocorticoids; immunology; inflammation; mouse; succinate; succinate dehydrogenase.
© 2023, Mateska et al.
Conflict of interest statement
IM, AW, EH, AS, CY, ET, NS, OK, MP, HA, HH, WK, BW, CT, AD, AW, KL, MP, TC, VA No competing interests declared
Figures

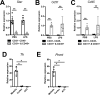
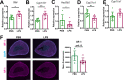
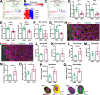

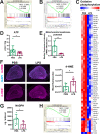

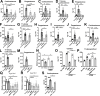
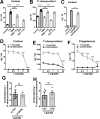
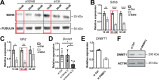
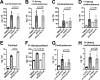
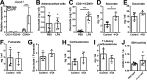

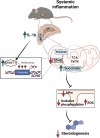
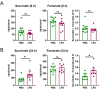
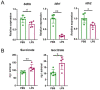
Comment in
-
Inflammation-induced adrenal dysfunction.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2023 Nov;19(11):622-623. doi: 10.1038/s41574-023-00896-3. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2023. PMID: 37696917 No abstract available.
References
-
- Aichler M, Borgmann D, Krumsiek J, Buck A, MacDonald PE, Fox JEM, Lyon J, Light PE, Keipert S, Jastroch M, Feuchtinger A, Mueller NS, Sun N, Palmer A, Alexandrov T, Hrabe de Angelis M, Neschen S, Tschöp MH, Walch A. N-acyl taurines and acylcarnitines cause an imbalance in insulin synthesis and secretion provoking β cell dysfunction in type 2 diabetes. Cell Metabolism. 2017;25:1334–1347. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.04.012. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

