Epigenetic Causes of Overgrowth Syndromes
- PMID: 37450557
- PMCID: PMC11032252
- DOI: 10.1210/clinem/dgad420
Epigenetic Causes of Overgrowth Syndromes
Abstract
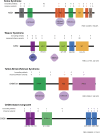
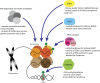
Human overgrowth disorders are characterized by excessive prenatal and/or postnatal growth of various tissues. These disorders often present with tall stature, macrocephaly, and/or abdominal organomegaly and are sometimes associated with additional phenotypic abnormalities such as intellectual disability and increased cancer risk. As the genetic etiology of these disorders have been elucidated, a surprising pattern has emerged. Multiple monogenic overgrowth syndromes result from variants in epigenetic regulators: variants in histone methyltransferases NSD1 and EZH2 cause Sotos syndrome and Weaver syndrome, respectively, variants in DNA methyltransferase DNMT3A cause Tatton-Brown-Rahman syndrome, and variants in chromatin remodeler CHD8 cause an autism spectrum disorder with overgrowth. In addition, very recently, a variant in histone reader protein SPIN4 was identified in a new X-linked overgrowth disorder. In this review, we discuss the genetics of these overgrowth disorders and explore possible common underlying mechanisms by which epigenetic pathways regulate human body size.
Keywords: WNT signaling; epigenetic modifications; histone; methylation; tall stature.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society 2023.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Co-occurrence of a maternally inherited DNMT3A duplication and a paternally inherited pathogenic variant in EZH2 in a child with growth retardation and severe short stature: atypical Weaver syndrome or evidence of a DNMT3A dosage effect?Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud. 2018 Aug 1;4(4):a002899. doi: 10.1101/mcs.a002899. Print 2018 Aug. Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud. 2018. PMID: 29802153 Free PMC article.
-
Further delineation of neuropsychiatric findings in Tatton-Brown-Rahman syndrome due to disease-causing variants in DNMT3A: seven new patients.Eur J Hum Genet. 2020 Apr;28(4):469-479. doi: 10.1038/s41431-019-0485-3. Epub 2019 Nov 4. Eur J Hum Genet. 2020. PMID: 31685998 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in Epigenetic Regulation Genes Are a Major Cause of Overgrowth with Intellectual Disability.Am J Hum Genet. 2017 May 4;100(5):725-736. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2017.03.010. Am J Hum Genet. 2017. PMID: 28475857 Free PMC article.
-
PRC2-complex related dysfunction in overgrowth syndromes: A review of EZH2, EED, and SUZ12 and their syndromic phenotypes.Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2019 Dec;181(4):519-531. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.c.31754. Epub 2019 Nov 14. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2019. PMID: 31724824 Review.
-
Sotos syndrome with marked overgrowth in three Japanese patients with heterozygous likely pathogenic NSD1 variants: case reports with review of literature.Endocr J. 2024 Jan 29;71(1):75-81. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ23-0502. Epub 2023 Nov 22. Endocr J. 2024. PMID: 37989294 Review.
Cited by
-
Growth disorders caused by variants in epigenetic regulators: progress and prospects.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Feb 2;15:1327378. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1327378. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38370361 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exome sequencing of patients with syndromic tall stature reveals four novel candidate genes.Endocr Connect. 2025 Jul 15;14(7):e250137. doi: 10.1530/EC-25-0137. Print 2025 Jul 1. Endocr Connect. 2025. PMID: 40577202 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of human overgrowth and use of omics in its diagnostics: chances and challenges.Front Genet. 2024 Jun 4;15:1382371. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1382371. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 38894719 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beckers A, Petrossians P, Hanson J, Daly AF. The causes and consequences of pituitary gigantism. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018;14(12):705‐720. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

