CASCADIA: a prospective community-based study protocol for assessing SARS-CoV-2 vaccine effectiveness in children and adults using a remote nasal swab collection and web-based survey design
- PMID: 37451722
- PMCID: PMC10350906
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-071446
CASCADIA: a prospective community-based study protocol for assessing SARS-CoV-2 vaccine effectiveness in children and adults using a remote nasal swab collection and web-based survey design
Abstract
Introduction: Although SARS-CoV-2 vaccines were first approved under Emergency Use Authorization by the Food and Drug Administration in late 2020 for adults, authorisation for young children 6 months to <5 years of age did not occur until 2022. These authorisations were based on clinical trials, understanding real-world vaccine effectiveness (VE) in the setting of emerging variants is critical. The primary goal of this study is to evaluate SARS-CoV-2 VE against infection among children aged >6 months and adults aged <50 years.
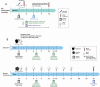
Methods: CASCADIA is a 4-year community-based prospective study of SARS-CoV-2 VE among 3500 adults and paediatric populations aged 6 months to 49 years in Oregon and Washington, USA. At enrolment and regular intervals, participants complete a sociodemographic questionnaire. Individuals provide a blood sample at enrolment and annually thereafter, with optional blood draws every 6 months and after infection and vaccination. Participants complete weekly self-collection of anterior nasal swabs and symptom questionnaires. Swabs are tested for SARS-CoV-2 and other respiratory pathogens by reverse transcription-PCR, with results of selected pathogens returned to participants; nasal swabs with SARS-CoV-2 detected will undergo whole genome sequencing. Participants who test positive for SARS-CoV-2 undergo serial swab collection every 3 days for 21 days. Serum samples are tested for SARS-CoV-2 antibody by binding and neutralisation assays.
Analysis: The primary outcome is SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cox regression models will be used to estimate the incidence rate ratio associated with SARS-CoV-2 vaccination among the paediatric and adult population, controlling for demographic factors and other potential confounders.
Ethics and dissemination: All study materials including the protocol, consent forms, data collection instruments, participant communication and recruitment materials, were approved by the Kaiser Permanente Interregional Institutional Review Board, the IRB of record for the study. Results will be disseminated through peer-reviewed publications, presentations, participant newsletters and appropriate general news media.
Keywords: COVID-19; epidemiology; paediatric infectious disease & immunisation.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: HYC reports consulting with Ellume, Pfizer, The Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, Glaxo Smith Kline, and Merck. HYC received research funding from Gates Ventures, Sanofi Pasteur, and support and reagents from Ellume and Cepheid outside of the submitted work. JAE reports research support from Gates Ventures, AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, and Pfizer, and consulting with Sanofi Pasteur, AstraZeneca, Teva Pharmaceuticals, and Meissa Vaccines, outside of the submitted work. ALN reports research funding from Pfizer and Vir Biotechnology, outside of the submitted work. JLK reports research funding from Vir Biotechnology, outside of the submitted work.
Figures

References
-
- 2020 WD-Gsoratmboc--M. 2020. Available: https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-genera... [Accessed 12 Jun 2022].
-
- Center JHCR . Coronavirus resource center 2022. Available: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html [Accessed 11 Jul 2023].
-
- Pediatrics AAo . Children and COVID-19: state-level data report. Available: https://www.aap.org/en/pages/2019-novel-coronavirus-covid-19-infections/... [Accessed 11 Jul 2023].
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
