Escherichia coli DNA repair helicase Lhr is also a uracil-DNA glycosylase
- PMID: 37452011
- PMCID: PMC10953399
- DOI: 10.1111/mmi.15123
Escherichia coli DNA repair helicase Lhr is also a uracil-DNA glycosylase
Abstract
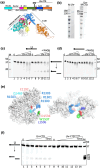
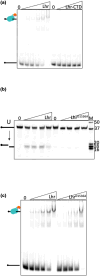
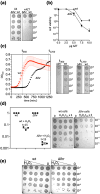
DNA glycosylases protect genetic fidelity during DNA replication by removing potentially mutagenic chemically damaged DNA bases. Bacterial Lhr proteins are well-characterized DNA repair helicases that are fused to additional 600-700 amino acids of unknown function, but with structural homology to SecB chaperones and AlkZ DNA glycosylases. Here, we identify that Escherichia coli Lhr is a uracil-DNA glycosylase (UDG) that depends on an active site aspartic acid residue. We show that the Lhr DNA helicase activity is functionally independent of the UDG activity, but that the helicase domains are required for fully active UDG activity. Consistent with UDG activity, deletion of lhr from the E. coli chromosome sensitized cells to oxidative stress that triggers cytosine deamination to uracil. The ability of Lhr to translocate single-stranded DNA and remove uracil bases suggests a surveillance role to seek and remove potentially mutagenic base changes during replication stress.
Keywords: DNA repair; DNA replication; glycosylase; helicase; uracil.
© 2023 The Authors. Molecular Microbiology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Almatarneh, M.H. , Flinn, C.G. & Poirier, R.A. (2008) Mechanisms for the deamination reaction of cytosine with H2O/OH(−) and 2H2O/OH(−): a computational study. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 48(4), 831–843. - PubMed
-
- Buttner, K. , Nehring, S. & Hopfner, K.P. (2007) Structural basis for DNA duplex separation by a superfamily‐2 helicase. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, 14(7), 647–652. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

