Surface characterization, electrochemical properties and in vitro biological properties of Zn-deposited TiO2 nanotube surfaces
- PMID: 37452093
- PMCID: PMC10349054
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-38733-2
Surface characterization, electrochemical properties and in vitro biological properties of Zn-deposited TiO2 nanotube surfaces
Abstract
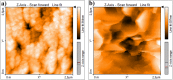
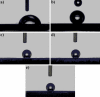
In this work, to improve antibacterial, biocompatible and bioactive properties of commercial pure titanium (cp-Ti) for implant applications, the Zn-deposited nanotube surfaces were fabricated on cp-Ti by using combined anodic oxidation (AO) and physical vapor deposition (PVD-TE) methods. Homogenous elemental distributions were observed through all surfaces. Moreover, Zn-deposited surfaces exhibited hydrophobic character while bare Ti surfaces were hydrophilic. Due to the biodegradable behavior of Zn on the nanotube surface, Zn-deposited nanotube surfaces showed higher corrosion current density than bare cp-Ti surface in SBF conditions as expected. In vitro biological properties such as cell viability, ALP activity, protein adsorption, hemolytic activity and antibacterial activity for Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria of all surfaces were investigated in detail. Cell viability, ALP activity and antibacterial properties of Zn-deposited nanotube surfaces were significantly improved with respect to bare cp-Ti. Moreover, hemolytic activity and protein adsorption of Zn-deposited nanotube surfaces were decreased. According to these results; a bioactive, biocompatible and antibacterial Zn-deposited nanotube surfaces produced on cp-Ti by using combined AO and PVD techniques can have potential for orthopedic and dental implant applications.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures









References
-
- Rios J, et al. Self-organized TiO2 nanotubes on Ti–Nb–Fe alloys for biomedical applications: Synthesis and characterization. Electrochem. Commun. 2022;138:107280. doi: 10.1016/j.elecom.2022.107280. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

