Targeting RNA oxidation by ISG20-mediated degradation is a potential therapeutic strategy for acute kidney injury
- PMID: 37452495
- PMCID: PMC10556188
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.07.008
Targeting RNA oxidation by ISG20-mediated degradation is a potential therapeutic strategy for acute kidney injury
Abstract
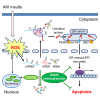
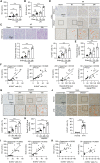
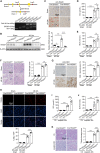
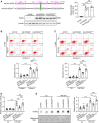
Oxidative stress plays a central role in the pathophysiology of acute kidney injury (AKI). Although RNA is one of the most vulnerable cell components to oxidative damage, it is unclear whether RNA oxidation is involved in the pathogenesis of AKI. In this study, we found that the level of RNA oxidation was significantly enhanced in kidneys of patients with acute tubular necrosis (ATN) and in the renal tubular epithelial cells (TECs) of mice with AKI, and oxidized RNA overload resulted in TEC injury. We further identified interferon-stimulated gene 20 (ISG20) as a novel regulator of RNA oxidation in AKI. Tubule-specific deficiency of ISG20 significantly aggravated renal injury and RNA oxidation in the ischemia/reperfusion-induced AKI mouse model and ISG20 restricted RNA oxidation in an exoribonuclease activity-dependent manner. Importantly, overexpression of ISG20 protected against oxidized RNA overproduction and renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice and ameliorated subsequent protein aggresome accumulation, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and unfolded protein response. Thus, our findings provide direct evidence that RNA oxidation contributes to the pathogenesis of AKI and that ISG20 importantly participates in the degradation of oxidized RNA, suggesting that targeting ISG20-handled RNA oxidation may be an innovative therapeutic strategy for AKI.
Keywords: ISG20; RNA oxidation; acute kidney injury; endoplasmic reticulum stress; unfolded protein response.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The protective effect of H151, a novel STING inhibitor, in renal ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2023 Jun 1;324(6):F558-F567. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00004.2023. Epub 2023 Apr 27. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37102684 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal miR-125b-5p deriving from mesenchymal stem cells promotes tubular repair by suppression of p53 in ischemic acute kidney injury.Theranostics. 2021 Mar 11;11(11):5248-5266. doi: 10.7150/thno.54550. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33859745 Free PMC article.
-
Connexin32 plays a crucial role in ROS-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress apoptosis signaling pathway in ischemia reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury.J Transl Med. 2018 May 4;16(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1493-8. J Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 29728112 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress in ischemic and nephrotoxic acute kidney injury.Ann Med. 2018 Aug;50(5):381-390. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2018.1489142. Epub 2018 Jul 11. Ann Med. 2018. PMID: 29895209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[The role of macrophage polarization and interaction with renal tubular epithelial cells in ischemia-reperfusion induced acute kidney injury].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2022 Feb 25;74(1):28-38. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2022. PMID: 35199123 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Oxysterol-binding protein-like 7 deficiency leads to ER stress-mediated apoptosis in podocytes and proteinuria.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2024 Sep 1;327(3):F340-F350. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00319.2023. Epub 2024 Jul 4. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38961844
-
S100A8/A9 high-expression macrophages mediate renal tubular epithelial cell damage in acute kidney injury following acute type A aortic dissection surgery.Front Mol Biosci. 2025 Apr 9;12:1530741. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1530741. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40270593 Free PMC article.
-
Coixol Protects Against Acute Kidney Injury by Reducing Cell Senescence.Biology (Basel). 2025 May 17;14(5):560. doi: 10.3390/biology14050560. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40427749 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting interferon-stimulated gene of 20 kDa protein (Isg20) inhibits ribosome biogenesis to ameliorate the progression of renal fibrosis.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 7;20(7):e0322639. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0322639. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40622935 Free PMC article.
-
RNA damage and its implications in genome stability.DNA Repair (Amst). 2025 Mar;147:103821. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2025.103821. Epub 2025 Mar 1. DNA Repair (Amst). 2025. PMID: 40043352 Review.
References
-
- Poulsen H.E., Specht E., Broedbaek K., Henriksen T., Ellervik C., Mandrup-Poulsen T., Tonnesen M., Nielsen P.E., Andersen H.U., Weimann A. RNA modifications by oxidation: a novel disease mechanism? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012;52:1353–1361. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

