Vagus nerve inflammation contributes to dysautonomia in COVID-19
- PMID: 37452829
- PMCID: PMC10412500
- DOI: 10.1007/s00401-023-02612-x
Vagus nerve inflammation contributes to dysautonomia in COVID-19
Abstract
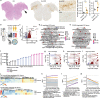
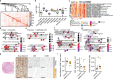
Dysautonomia has substantially impacted acute COVID-19 severity as well as symptom burden after recovery from COVID-19 (long COVID), yet the underlying causes remain unknown. Here, we hypothesized that vagus nerves are affected in COVID-19 which might contribute to autonomic dysfunction. We performed a histopathological characterization of postmortem vagus nerves from COVID-19 patients and controls, and detected SARS-CoV-2 RNA together with inflammatory cell infiltration composed primarily of monocytes. Furthermore, we performed RNA sequencing which revealed a strong inflammatory response of neurons, endothelial cells, and Schwann cells which correlated with SARS-CoV-2 RNA load. Lastly, we screened a clinical cohort of 323 patients to detect a clinical phenotype of vagus nerve affection and found a decreased respiratory rate in non-survivors of critical COVID-19. Our data suggest that SARS-CoV-2 induces vagus nerve inflammation followed by autonomic dysfunction which contributes to critical disease courses and might contribute to dysautonomia observed in long COVID.
Keywords: COVID-19; Dysautonomia; Neuroinflammation; Vagus nerve.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Carmona-Torre F, Mínguez-Olaondo A, López-Bravo A, Tijero B, Grozeva V, Walcker M, Azkune-Galparsoro H, López de Munain A, Alcaide AB, Quiroga J, del Pozo JL, Gómez-Esteban JC. Dysautonomia in COVID-19 patients: a narrative review on clinical course, diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. Front Neurol. 2022 doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.886609. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dejanovic B, Wu T, Tsai M-C, Graykowski D, Gandham VD, Rose CM, Bakalarski CE, Ngu H, Wang Y, Pandey S, Rezzonico MG, Friedman BA, Edmonds R, De Mazière A, Rakosi-Schmidt R, Singh T, Klumperman J, Foreman O, Chang MC, Xie L, Sheng M, Hanson JE. Complement C1q-dependent excitatory and inhibitory synapse elimination by astrocytes and microglia in Alzheimer’s disease mouse models. Nat Aging. 2022;2:837–850. doi: 10.1038/s43587-022-00281-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Delorey TM, Ziegler CGK, Heimberg G, Normand R, Yang Y, Segerstolpe Å, Abbondanza D, Fleming SJ, Subramanian A, Montoro DT, Jagadeesh KA, Dey KK, Sen P, Slyper M, Pita-Juárez YH, Phillips D, Biermann J, Bloom-Ackermann Z, Barkas N, Ganna A, Gomez J, Melms JC, Katsyv I, Normandin E, Naderi P, Popov YV, Raju SS, Niezen S, Tsai LT-Y, Siddle KJ, Sud M, Tran VM, Vellarikkal SK, Wang Y, Amir-Zilberstein L, Atri DS, Beechem J, Brook OR, Chen J, Divakar P, Dorceus P, Engreitz JM, Essene A, Fitzgerald DM, Fropf R, Gazal S, Gould J, Grzyb J, Harvey T, Hecht J, Hether T, Jané-Valbuena J, Leney-Greene M, Ma H, McCabe C, McLoughlin DE, Miller EM, Muus C, Niemi M, Padera R, Pan L, Pant D, Pe’er C, Pfiffner-Borges J, Pinto CJ, Plaisted J, Reeves J, Ross M, Rudy M, Rueckert EH, Siciliano M, Sturm A, Todres E, Waghray A, Warren S, Zhang S, Zollinger DR, Cosimi L, Gupta RM, Hacohen N, Hibshoosh H, Hide W, Price AL, Rajagopal J, Tata PR, Riedel S, Szabo G, Tickle TL, Ellinor PT, Hung D, Sabeti PC, Novak R, Rogers R, Ingber DE, Jiang ZG, Juric D, Babadi M, Farhi SL, Izar B, Stone JR, Vlachos IS, Solomon IH, Ashenberg O, Porter CBM, Li B, Shalek AK, Villani A-C, Rozenblatt-Rosen O, Regev A, COVID-19 tissue atlases reveal SARS-CoV-2 pathology and cellular targets. Nature. 2021;595:107–113. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03570-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

