ReIGNITE Radiation Therapy Boost: A Prospective, International Study of Radiation Oncologists' Accuracy in Contouring Prostate Tumors for Focal Radiation Therapy Boost on Conventional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Alone or With Assistance of Restriction Spectrum Imaging
- PMID: 37453559
- PMCID: PMC11088932
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2023.07.004
ReIGNITE Radiation Therapy Boost: A Prospective, International Study of Radiation Oncologists' Accuracy in Contouring Prostate Tumors for Focal Radiation Therapy Boost on Conventional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Alone or With Assistance of Restriction Spectrum Imaging
Abstract
Purpose: In a phase III randomized trial, adding a radiation boost to tumor(s) visible on MRI improved prostate cancer (PCa) disease-free and metastasis-free survival without additional toxicity. Radiation oncologists' ability to identify prostate tumors is critical to widely adopting intraprostatic tumor radiotherapy boost for patients. A diffusion MRI biomarker, called the Restriction Spectrum Imaging restriction score (RSIrs), has been shown to improve radiologists' identification of clinically significant PCa. We hypothesized that (1) radiation oncologists would find accurately delineating PCa tumors on conventional MRI challenging and (2) using RSIrs maps would improve radiation oncologists' accuracy for PCa tumor delineation.
Methods and materials: In this multi-institutional, international, prospective study, 44 radiation oncologists (participants) and 2 expert radiologists (experts) contoured prostate tumors on 39 total patient cases using conventional MRI with or without RSIrs maps. Participant volumes were compared to the consensus expert volumes. Contouring accuracy metrics included percent overlap with expert volume, Dice coefficient, conformal number, and maximum distance beyond expert volume.
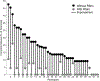
Results: 1604 participant volumes were produced. 40 of 44 participants (91%) completely missed ≥1 expert-defined target lesion without RSIrs, compared to 13 of 44 (30%) with RSIrs maps. On conventional MRI alone, 134 of 762 contour attempts (18%) completely missed the target, compared to 18 of 842 (2%) with RSIrs maps. Use of RSIrs maps improved all contour accuracy metrics by approximately 50% or more. Mixed effects modeling confirmed that RSIrs maps were the main variable driving improvement in all metrics. System Usability Scores indicated RSIrs maps significantly improved the contouring experience (72 vs. 58, p < 0.001).
Conclusions: Radiation oncologists struggle with accurately delineating visible PCa tumors on conventional MRI. RSIrs maps improve radiation oncologists' ability to target MRI-visible tumors for prostate tumor boost.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement:
AJL reports consulting for MIM Software. MEH reports honoraria from Multimodal Imaging Services Corporation and research funding from GE Healthcare. RRP has an equity interest in CorTech Labs and Curemetrix, serves on the Scientific Advisory Board of Imagine Scientific, and receives research funding from GE Healthcare. AMD is a Founder of and holds equity in CorTechs Labs, Inc, and serves on its Scientific Advisory Board. He is a member of the Scientific Advisory Board of Human Longevity, Inc. and receives funding through research agreements with GE Healthcare. TMS reports honoraria from Multimodal Imaging Services Corporation, Varian Medical Systems, and WebMD; he has an equity interest in CorTechs Labs, Inc. and also serves on its Scientific Advisory Board; he has received in-kind research support from GE Healthcare via a research agreement with the University of California San Diego. These companies might potentially benefit from the research results. The terms of these arrangements have been reviewed and approved by the University of California San Diego in accordance with its conflict-of-interest policies.
Figures

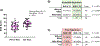
References
-
- Kerkmeijer LGW, Groen VH, Pos FJ, et al. The FLAME trial: benefit of a focal boost for prostate cancer on biochemical disease-free survival. Radiotherapy and Oncology 2020;152:Supplement 1:0360–0361.
-
- Kerkmeijer L, Groen V, Pos FJ, et al. Five-Year Toxicity after EBRT for Localized Prostate Cancer with or without a Simultaneously Integrated Focal Boost up to 95Gy: Results of a Randomized Controlled Trial. International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics 2020;108(3):S61–S62. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2020.07.2193. - DOI
-
- Anwar M, Westphalen AC, Jung AJ, et al. Role of endorectal MR imaging and MR spectroscopic imaging in defining treatable intraprostatic tumor foci in prostate cancer: Quantitative analysis of imaging contour compared to whole-mount histopathology. Radiotherapy and Oncology 2014;110(2):303–308. DOI: 10.1016/j.radonc.2013.12.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

