Structural brain network analysis in occipital lobe epilepsy
- PMID: 37454057
- PMCID: PMC10349483
- DOI: 10.1186/s12883-023-03326-z
Structural brain network analysis in occipital lobe epilepsy
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to analyze the structural brain network in patients with occipital lobe epilepsy (OLE) and investigate the differences in structural brain networks between patients with OLE and healthy controls.
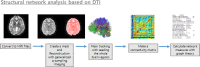
Methods: Patients with OLE and healthy controls with normal brain MRI findings were enrolled. They underwent diffusion tensor imaging using a 3.0T MRI scanner, and we computed the network measures of global and local structural networks in patients with OLE and healthy controls using the DSI studio program. We compared network measures between the groups.
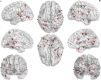
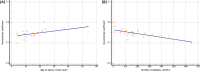
Results: We enrolled 23 patients with OLE and 42 healthy controls. There were significant differences in the global structural network between patients with OLE and healthy controls. The assortativity coefficient (-0.0864 vs. -0.0814, p = 0.0214), mean clustering coefficient (0.0061 vs. 0.0064, p = 0.0203), global efficiency (0.0315 vs. 0.0353, p = 0.0086), and small-worldness index (0.0001 vs. 0.0001, p = 0.0175) were lower, whereas the characteristic path length (59.2724 vs. 53.4684, p = 0.0120) was higher in patients with OLE than those in the healthy controls. There were several nodes beyond the occipital lobe that showed significant differences in the local structural network between the groups. In addition, the assortativity coefficient was negatively correlated with the duration of epilepsy (r=-0.676, p = 0.001).
Keywords: Diffusion tensor imaging; Epilepsy; Occipital lobe.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Neither of the authors has any conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glymphatic system dysfunction in patients with occipital lobe epilepsy.J Neuroimaging. 2023 May-Jun;33(3):455-461. doi: 10.1111/jon.13083. Epub 2023 Jan 10. J Neuroimaging. 2023. PMID: 36627235
-
Reorganization of brain networks in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy and comorbid headache.Epilepsy Behav. 2023 Mar;140:109101. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2023.109101. Epub 2023 Feb 1. Epilepsy Behav. 2023. PMID: 36736237
-
Progressive topological disorganization of brain network in focal epilepsy.Acta Neurol Scand. 2018 Apr;137(4):425-431. doi: 10.1111/ane.12899. Epub 2018 Jan 17. Acta Neurol Scand. 2018. PMID: 29344935
-
Thalamic nuclei volumes and intrinsic thalamic network in patients with occipital lobe epilepsy.Brain Behav. 2023 Apr;13(4):e2968. doi: 10.1002/brb3.2968. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Brain Behav. 2023. PMID: 36924055 Free PMC article.
-
Occipital lobe seizures and epilepsies.J Clin Neurophysiol. 2012 Oct;29(5):397-407. doi: 10.1097/WNP.0b013e31826c98fe. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2012. PMID: 23027097 Review.
Cited by
-
Small-vessel-disease-induced white matter damage in occipital lobe epilepsy.Front Neurol. 2025 Feb 11;16:1538598. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1538598. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40007738 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of individual's age on the characteristics of brain effective connectivity.Geroscience. 2025 Apr;47(2):2455-2474. doi: 10.1007/s11357-024-01436-1. Epub 2024 Nov 16. Geroscience. 2025. PMID: 39549197 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

