Optimization of energy recovery efficiency from sweet sorghum stems by ethanol and methane fermentation processes coupling
- PMID: 37455672
- PMCID: PMC10353323
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2023.2234135
Optimization of energy recovery efficiency from sweet sorghum stems by ethanol and methane fermentation processes coupling
Abstract
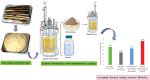
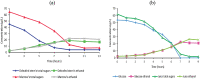
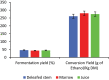
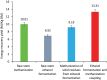
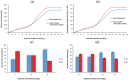
Taken separately, a single sweet sorghum stem bioconversion process for bioethanol and biomethane production only leads to a partial conversion of organic matter. The direct fermentation of crushed whole stem coupled with the methanization of the subsequent solid residues in a two-stage process was experimented to improve energy bioconversion yield, efficiency, and profitability. The raw stalk calorific value was 17,144.17 kJ/kg DM. Fermentation step performed using Saccharomyces cerevisiae resulted in a bioconversion yield of 261.18 g Eth/kg DM, i.e. an energy recovery efficiency of 6921.27 kJ/kg DM. The methanogenic potentials were 279 and 256 LCH4/kg DM, respectively, for raw stem and fermentation residues, i.e. energy yields of 10,013.31 and 9187.84 kJ/kg DM, respectively. Coupling processes have significantly increased yield and made it possible to reach 13,309.57 kJ/kg DM, i.e. 77.63% of raw stem energy recovery yield, compared to 40.37% and 58.40%, respectively, for single fermentation and methanization processes.
Keywords: Sorghum; bioconversion; bioenergy; biomass; energy efficiency; ethanol; methane.
Plain language summary
Sweet sorghum stem is a viable feedstock source for efficient coproduction of ethanol and methaneSorghum stems calorific value determination revealed an energy potential of 17.15 MJ/kg DMEnergy recovery by single methanization yielded 18.03% more than ethanol fermentationCoupling processes has significantly increased energy recovery yield and profitability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- IEA , 2021. World Energy Outlook 2021. IEA, Paris. https://www.iea.org/reports/world-energy-outlook-2021.
-
- IEA , 2022. World Energy Investment 2022. IEA, Paris. https://www.iea.org/reports/world-energy-investment-2022.
-
- Kevser M, Tekbaş M, Doğan M, et al. Nexus among biomass energy consumption, economic growth, and financial development: Evidence from selected 15 countries. Energy Rep. 2022;8:8372–8380. doi: 10.1016/j.egyr.2022.06.033 - DOI
-
- Zhang CW, Wen H, Zheng J, et al. A combination of evaporation and chemical preservation for long-term storage of fresh sweet sorghum juice and subsequent bioethanol production. J Food Process Pres. 2018;42:13825. doi: 10.1111/jfpp.13825 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
