Peer Teaching in Undergraduate Medical Education: What are the Learning Outputs for the Student-Teachers? A Systematic Review
- PMID: 37455859
- PMCID: PMC10349571
- DOI: 10.2147/AMEP.S401766
Peer Teaching in Undergraduate Medical Education: What are the Learning Outputs for the Student-Teachers? A Systematic Review
Abstract
Introduction: To achieve quality in medical education, peer teaching, understood as students taking on roles as educators for peers, is frequently used as a teaching intervention. While the benefits of peer teaching for learners and faculty are described in detail in the literature, less attention is given to the learning outputs for the student-teachers. This systematic review focuses on the learning outputs for medical undergraduates acting as student-teachers in the last decade (2012-2022).
Aim: Our aim is to describe what learning outputs student-teachers have from peer teaching, and map what research methods are used to assess the outputs. We defined learning outputs in a broad sense, including all types of learning experiences, intended and non-intended, associated with being a peer teacher.
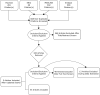
Methods: A literature search was conducted in four electronic databases. Title, abstract and full text were screened by 8 independent reviewers and selection was based on predefined eligibility criteria. We excluded papers not describing structured peer teaching interventions with student-teachers in a formalized role. From the included articles we extracted information about the learning outputs of being a student-teacher as medical undergraduate.
Results: From 668 potential titles, 100 were obtained as full-texts, and 45 selected after close examination, group deliberation, updated search and quality assessment using MERSQI score (average score 10/18). Most articles reported learning outputs using mixed methods (67%). Student-teachers reported an increase in subject-specific learning (62%), pedagogical knowledge and skills (49%), personal outputs (31%) and generic skills (38%). Most articles reported outputs using self-reported data (91%).
Conclusion: Although there are few studies that systematically investigate student-teachers learning outputs, evidence suggests that peer teaching offers learning outputs for the student-teachers and helps them become better physicians. Further research is needed to enhance learning outputs for student-teachers and systematically investigate student-teachers' learning outputs and its impact on student-teachers.
Keywords: medical school; medical student; peer teacher; peer-assisted learning.
© 2023 Tanveer et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Medical students-as-teachers: a systematic review of peer-assisted teaching during medical school.Adv Med Educ Pract. 2011 Jun 23;2:157-72. doi: 10.2147/AMEP.S14383. Print 2011. Adv Med Educ Pract. 2011. PMID: 23745087 Free PMC article.
-
Peer teachers as ultrasound instructors? - a systematic literature review of peer teaching concepts in undergraduate ultrasound education.BMC Med Educ. 2024 Nov 26;24(1):1369. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-06345-7. BMC Med Educ. 2024. PMID: 39593017 Free PMC article.
-
When learners become teachers: a review of peer teaching in medical student education.Fam Med. 2014 Nov-Dec;46(10):783-7. Fam Med. 2014. PMID: 25646829 Review.
-
Student teaching: views of student near-peer teachers and learners.Med Teach. 2007 Sep;29(6):583-90. doi: 10.1080/01421590701583824. Med Teach. 2007. PMID: 17922356
-
Student and educator experiences of maternal-child simulation-based learning: a systematic review of qualitative evidence protocol.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Jan;13(1):14-26. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-1694. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26447004
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of Peer-Assisted Learning in health professional education: a scoping review of systematic reviews.BMC Med Educ. 2024 Dec 18;24(1):1467. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-06434-7. BMC Med Educ. 2024. PMID: 39695653 Free PMC article.
-
From Tutor to Future Educator: Investigating the Role of Peer-Peer Tutoring in Shaping Careers in Medical Education.Med Sci Educ. 2024 Sep 9;35(1):179-192. doi: 10.1007/s40670-024-02161-2. eCollection 2025 Feb. Med Sci Educ. 2024. PMID: 40144120 Free PMC article.
-
How can peer teaching influence the development of medical students? a descriptive, longitudinal interview study.BMC Med Educ. 2023 Nov 13;23(1):861. doi: 10.1186/s12909-023-04801-4. BMC Med Educ. 2023. PMID: 37957668 Free PMC article.
-
Learning from medical errors.CVIR Endovasc. 2024 Jan 10;7(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s42155-023-00406-6. CVIR Endovasc. 2024. PMID: 38197983 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Unpacking the perceptions and experiences of student facilitators in interprofessional education: a qualitative study.Med Educ Online. 2024 Dec 31;29(1):2330257. doi: 10.1080/10872981.2024.2330257. Epub 2024 Mar 17. Med Educ Online. 2024. PMID: 38493489 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cambridge Dictionary [online dictionary]. Cambridge University Press; 2022. Available from: https://dictionary.cambridge.org/. Accessed June 22, 2022.
-
- Stigmar M. Peer-to-peer teaching in higher education: a critical literature review. Mentor Tutoring. 2016;24(2):124–136. doi:10.1080/13611267.2016.1178963 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources