Sarcopenic obesity: epidemiology, pathophysiology, cardiovascular disease, mortality, and management
- PMID: 37455897
- PMCID: PMC10344359
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1185221
Sarcopenic obesity: epidemiology, pathophysiology, cardiovascular disease, mortality, and management
Abstract
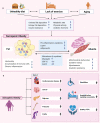
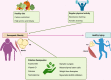
Sarcopenic obesity is defined as the coexistence of sarcopenia and obesity in the same individual, characterized by of the co-presence of body fat accumulation and muscle loss. This condition is currently a major concern as it is associated with frailty and disabilities such as cardiovascular disease, fractures, dementia, cancer, and increased all-cause mortality. Particularly, older individuals remain at risk of sarcopenic obesity. Progress at several levels is needed to improve the global prognostic outlook for this condition, including the elaboration and implementation of a more uniform definition that may favor the identification and specification of prevalence by age group. Furthermore, improvements in the understanding of the pathogenesis of sarcopenic obesity may lead to the development of more specific therapeutic interventions to improve prognosis. We reviewed the knowledge on sarcopenic obesity and its associations with cardiovascular diseases and mortality.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease; endocrine; obesity; pathogenesis; sarcopenia.
Copyright © 2023 Wei, Nguyen, Zhang, Ryu and Gariani.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Leong DP, Teo KK, Rangarajan S, Lopez-Jaramillo P, Avezum A, Jr., Orlandini A, et al. Prospective urban rural epidemiology study, prognostic value of grip strength: findings from the prospective urban rural epidemiology (PURE) study. Lancet (2015) 386:266–73. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)62000-6 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

