Research trends in cholangiocarcinoma treatments during the last 3 decades
- PMID: 37455974
- PMCID: PMC10338968
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17100
Research trends in cholangiocarcinoma treatments during the last 3 decades
Erratum in
-
Erratum to "Research trends in cholangiocarcinoma treatments during the last 3 decades" [Heliyon 9(7) (July 2023) e17100].Heliyon. 2023 Aug 29;9(9):e19443. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19443. eCollection 2023 Sep. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37809857 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Over the past 30 years, numerous studies have focused on the treatment of cholangiocarcinoma (CCA), and these treatments have greatly evolved.
Objectives: To better understand the research trends, we evaluated the most influential publications and attempted to identify their characteristics using bibliometric methods.
Methods: The most influential publications were identified from the Clarivate Analytics Web of Science Core Collection database. The general characteristics of included papers were identified, and the research trends were explored via the bibliometric method.
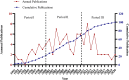
Results: The average total number of citations for of the listed publications were 312 (range from 165 to 1922). The highest number of papers were published during period II (2001-2010, n = 50), followed by period III (2011-2020, n = 28), and period I (1991-2000, n = 22). The United States and Germany have made remarkable achievements in this field. Institutionally, Mayo Clinic and Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center were the leading institutions, with Blumgart and Zhu from the United States being the most influential authors. Close collaboration was established between the leading countries, institutions, and authors. The Annals of Surgery contributed the most to the papers with the highest total number of citations. Surgery predominated during period I (n = 14, 63.6%), with a gradual decline occurring during periods II (n = 19, 41.3%, P = 0.085) and period III (n = 3, 9.4%, P = 0.002). Contrastingly, the number of publications related to systemic therapy has increased significantly since period II and peaked in period III.
Conclusions: Surgery remains the most important treatment for CCA. However systemic therapy has become a research and clinical application hotspot. These findings will contribute to the translation of treatments for CCA and provide researchers with relevant research directions.
Keywords: Bibliometric analysis; Cholangiocarcinoma; Surgery; Systemic therapy; Targeted therapy.
© 2023 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures







References
-
- Khan S.A., Tavolari S., Brandi G. Cholangiocarcinoma: Epidemiology and risk factors. Liver Int. 2019;39(Suppl 1):19–31. - PubMed
-
- Rizzo A., Brandi G. First-line chemotherapy in advanced biliary tract cancer ten years after the ABC-02 trial: "and yet it moves!". Cancer Treat Res Commun. 2021;27 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

