CSL362 potently and specifically depletes pDCs invitro and ablates SLE-immune complex-induced IFN responses
- PMID: 37456846
- PMCID: PMC10338305
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107173
CSL362 potently and specifically depletes pDCs invitro and ablates SLE-immune complex-induced IFN responses
Abstract
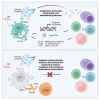
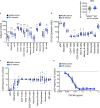
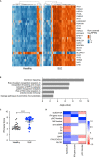
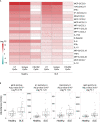
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease with significant morbidity and mortality. Type I interferon (IFN) drives SLE pathology and plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) are potent producers of IFN; however, the specific effects of pDC depletion have not been demonstrated. We show CD123 was highly expressed on pDCs and the anti-CD123 antibody CSL362 potently depleted pDCs in vitro. CSL362 pre-treatment abrogated the induction of IFNα and IFN-induced gene transcription following stimulation with SLE patient-derived serum or immune complexes. RNA transcripts induced in pDCs by ex vivo stimulation with TLR ligands were reflected in gene expression profiles of SLE blood, and correlated with disease severity. TLR ligand-induced protein production by SLE patient peripheral mononuclear cells was abrogated by CSL362 pre-treatment including proteins over expressed in SLE patient serum. These findings implicate pDCs as key drivers in the cellular activation and production of soluble factors seen in SLE.
Keywords: Health sciences; Immunology; Pathophysiology.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was done as part of study by CSL Limited and Janssen/Johnson and Johnson. K.A.M., N.W., M.N., and C.G. are employees and shareholders of CSL Limited. During the study T.Y.T. was an employee of CSL. During the study J.B., T.S., B.L., and J.J. were employees and/or shareholders of Johnson and Johnson. I.W. has acted as a scientific advisor to CSL and his laboratory has received funding for pre-clinical evaluation of CSL362. A.H. reports sponsorship of the Australian Lupus Registry and Biobank which is chaired by A.H. received from Janssen. A.H. also reports meeting support and consulting fees from Janssen. E.M. reports research support from CSL and Janssen.
Figures


References
-
- Bauer J.W., Baechler E.C., Petri M., Batliwalla F.M., Crawford D., Ortmann W.A., Espe K.J., Li W., Patel D.D., Gregersen P.K., et al. Elevated serum levels of interferon-regulated chemokines are biomarkers for active human systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS Med. 2006;3:e491. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0030491. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ytterberg S.R., Schnitzer T.J. Serum interferon levels in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982;25:401–406. - PubMed
-
- Hervier B., Beziat V., Haroche J., Mathian A., Lebon P., Ghillani-Dalbin P., Musset L., Debré P., Amoura Z., Vieillard V. Phenotype and function of natural killer cells in systemic lupus erythematosus: excess interferon-gamma production in patients with active disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63:1698–1706. doi: 10.1002/art.30313. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

