Transcranial direct current stimulation over left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex facilitates auditory-motor integration for vocal pitch regulation
- PMID: 37457017
- PMCID: PMC10347532
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1208581
Transcranial direct current stimulation over left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex facilitates auditory-motor integration for vocal pitch regulation
Abstract
Background: A growing body of literature has implicated the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) in the online monitoring of vocal production through auditory feedback. Specifically, disruption of or damage to the left DLPFC leads to exaggerated compensatory vocal responses to altered auditory feedback. It is conceivable that enhancing the cortical excitability of the left DLPFC may produce inhibitory influences on vocal feedback control by reducing vocal compensations.
Methods: We used anodal transcranial direct current stimulation (a-tDCS) to modulate cortical excitability of the left DLPFC and examined its effects on auditory-motor integration for vocal pitch regulation. Seventeen healthy young adults vocalized vowel sounds while hearing their voice pseudo-randomly pitch-shifted by ±50 or ±200 cents, either during (online) or after (offline) receiving active or sham a-tDCS over the left DLPFC.
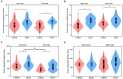
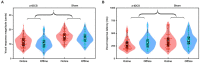
Results: Active a-tDCS over the left DLPFC led to significantly smaller peak magnitudes and shorter peak times of vocal compensations for pitch perturbations than sham stimulation. In addition, this effect was consistent regardless of the timing of a-tDCS (online or offline stimulation) and the size and direction of the pitch perturbation.
Conclusion: These findings provide the first causal evidence that a-tDCS over the left DLPFC can facilitate auditory-motor integration for compensatory adjustment to errors in vocal output. Reduced and accelerated vocal compensations caused by a-tDCS over left DLPFC support the hypothesis of a top-down neural mechanism that exerts inhibitory control over vocal motor behavior through auditory feedback.
Keywords: auditory feedback; left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex; speech motor control; top–down modulation; transcranial direct current stimulation.
Copyright © 2023 Chang, Peng, Zhao, Chen, Li, Wu, Liu and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Angius L., Santarnecchi E., Pascual-Leone A., Marcora S. M. (2019). Transcranial direct current stimulation over the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex improves inhibitory control and endurance performance in healthy individuals. Neuroscience 419, 34–45. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.08.052, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Behroozmand R., Johari K., Bridwell K., Hayden C., Fahey D., den Ouden D. B. (2020). Modulation of vocal pitch control through high-definition transcranial direct current stimulation of the left ventral motor cortex. Exp. Brain Res. 238, 1525–1535. doi: 10.1007/s00221-020-05832-9, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

