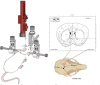
Arduino based intra-cerebral microinjector device for neuroscience research
- PMID: 37457306
- PMCID: PMC10344678
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ohx.2023.e00446
Arduino based intra-cerebral microinjector device for neuroscience research
Abstract
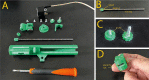
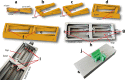
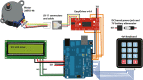
Stereotaxic surgery is a less invasive form of surgery that uses a three-dimensional coordinate system to place instruments at a specific location in the brain. Through this type of surgery, one can place needles among other tools within the structures of the brain. Therefore, injections can be given in order to deliver substances that cannot cross the blood-brain barrier. The two most important parameters of the microinjection to control are volume and speed. The volume should not be so large that it displaces the brain tissue and tears it. The injection speed must also be slow so that the liquid that comes out of the syringe can diffuse into the tissue without displacing it and damaging it. Thus, the objectives of the present work are: 1) To develop not a 3D printed prototype but an end-user device. 2) The device must be for animal research only. 3) It must have the same precision in volume and speed as commercial devices. 4) It must be adjustable for microsyringes from 0.5 µl to 1 ml. 5) It must be possible to place it directly on the stereotaxic surgery apparatus and to use it separately. 6) The price must be substantially lower than that of the commercial devices.
Keywords: Arduino; Intracerebral injection; Microinjection; Neuroscience; Open hardware; Stereotaxic surgery.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures








Similar articles
-
An inhalation anesthetic device for stereotaxic operation on mouse pups.J Neurosci Methods. 2015 Mar 30;243:63-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2015.01.025. Epub 2015 Jan 31. J Neurosci Methods. 2015. PMID: 25647713
-
MRI-guided stereotaxic targeting in pigs based on a stereotaxic localizer box fitted with an isocentric frame and use of SurgiPlan computer-planning software.J Neurosci Methods. 2009 Oct 15;183(2):119-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2009.06.019. Epub 2009 Jun 24. J Neurosci Methods. 2009. PMID: 19559051
-
The effect of jet speed on large volume jet injection.J Control Release. 2018 Jun 28;280:51-57. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.04.054. Epub 2018 Apr 30. J Control Release. 2018. PMID: 29723614
-
Discrepancies in stereotaxic coordinate publications and improving precision using an animal-specific atlas.J Neurosci Methods. 2017 Jun 1;284:15-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2017.03.019. Epub 2017 Apr 7. J Neurosci Methods. 2017. PMID: 28392415 Review.
-
Constructing the rodent stereotaxic brain atlas: a survey.Sci China Life Sci. 2022 Jan;65(1):93-106. doi: 10.1007/s11427-020-1911-9. Epub 2021 Apr 13. Sci China Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 33860452 Review.
Cited by
-
xDev: a mixed-signal, software-defined neurotechnology interface platform for accelerated system development.J Neural Eng. 2025 Mar 11;22(2):026012. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/adb7bf. J Neural Eng. 2025. PMID: 40066693 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rahman M., Murad G.J.A., Mocco J. Early history of the stereotactic apparatus in neurosurgery. Neurosurg. Focus. 2009;27:E12. - PubMed
-
- Kirschner M. Die Punktionstechnik und die Elektrokoagulation des Ganglion Gasseri. Arch Klin Chir. 1933;176:581–620. ISSN 0365–3706.
-
- K. Shimizu, A. Gupta , P.K. Brastianos , H. Wakimoto, Anatomy-oriented stereotactic approach to cerebrospinal fluid collection in mice. Brain Res., 1, (2022)1774:147706. 10.1016/j.brainres.2021.147706. Epub 2021 Oct 31. PMID: 34732332. - PubMed
-
- Hect J.L., Alattar A.A., Harford E.E., Reecher H., Fernandes D.T., Esplin N., McDowell M., Abel T.J. Stereotactic laser interstitial thermal therapy for the treatment of pediatric drug-resistant epilepsy: indications, techniques, and safety. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2022;38(5):961–970. doi: 10.1007/s00381-022-05491-x. Epub 2022 Mar 11 PMID: 35274185. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bjarkam C.R., Glud A.N., Margolin L., Reinhart K., Franklin R., Deding D. Safety and function of a new clinical intracerebral microinjection instrument for stem cells and therapeutics examined in the Göttingen Minipig. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2010;88:56–63. doi: 10.1159/000268743. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

