Gentiopicroside-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles Inhibit TNF-α-Induced Proliferation and Inflammatory Response in HaCaT Keratinocytes and Ameliorate Imiquimod-Induced Dermatitis Lesions in Mice
- PMID: 37457802
- PMCID: PMC10348341
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S406649
Gentiopicroside-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles Inhibit TNF-α-Induced Proliferation and Inflammatory Response in HaCaT Keratinocytes and Ameliorate Imiquimod-Induced Dermatitis Lesions in Mice
Abstract
Purpose: In this study, we aimed to report the biological characteristics of the first successful synthesis of gentiopicroside-loaded chitosan nanoparticles and to evaluate the therapeutic effects and preliminary mechanisms of gentiopicrin-loaded chitosan on psoriasis-like cell and mouse models.
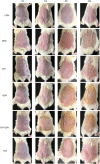
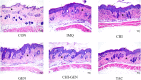
Methods: Gentiopicroside-loaded chitosan nanoparticles (CHI-GEN) were prepared, and their biological characteristics were evaluated. HaCaT keratinocytes were stimulated with TNF-α to establish a psoriatic keratinocyte model. MTT assay and flow cytometry were used to measure cell viability and apoptosis, respectively. mRNA levels of K17, VEGF A, and IL-6 and IL-23A were detected using qRT-PCR. These tests were used to preliminarily assess the effects of CHI-GEN on keratinocyte proliferation and inflammation. Imiquimod was used to construct a psoriasis-like mice model. The severity of psoriasis was scored based on the psoriasis area severity index (PASI), H&E staining was used to observe the histological changes and the level of inflammation and cell proliferation of skin lesions was evaluated by measuring the mRNA levels of K17, IL-23A, and IL-17A using qRT-PCR.
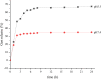
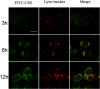
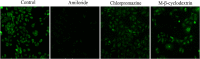
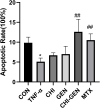
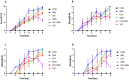
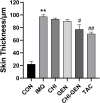
Results: The average particle size of CHI-GEN nanoparticles was approximately 100 nm, and the zeta potential was 2.69 ± 0.87 mV. The cumulative release was 67.2% in solutions of pH 5.5 at 24 h. GEN reduced TNF-α-induced excessive proliferation of HaCaT keratinocytes and downregulated mRNA levels of K17, VEGF A, and inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and IL-23A, which was more obvious in the CHI-GEN treatment group. Additionally, CHI-GEN significantly improved the severity of skin lesions in psoriasis-like mice and downregulated the mRNA expressions of IL-6, IL-23A, and IL-17A in mice skin lesions.
Conclusion: In conclusion, we successfully prepared gentiopicrin-chitosan nanoparticles. Our results show that these nanoparticles have anti-psoriasis activity, inhibits keratinocyte proliferation and improves symptoms in psoriasis model mice and can be used to develop an effective strategy for the treatment of psoriasis.
Keywords: chitosan; chitosan-loaded nano cream for external use; gentiopicroside; nanoparticles; proliferation and inflammation; psoriasis.
© 2023 Zhao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures





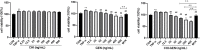



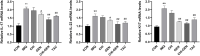
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

