Targeting EP2 Receptor for Drug Discovery: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats (SWOT) Analysis
- PMID: 37458373
- PMCID: PMC10388357
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c00655
Targeting EP2 Receptor for Drug Discovery: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats (SWOT) Analysis
Abstract
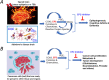
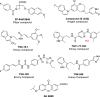
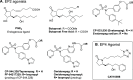
Cyclooxygenase-1 and -2 (COX1 and COX2) derived endogenous ligand prostaglandin-E2 (PGE2) triggers several physiological and pathological conditions. It mediates signaling through four G-protein coupled receptors, EP1, EP2, EP3, and EP4. Among these, EP2 is expressed throughout the body including the brain and uterus. The functional role of EP2 has been extensively studied using EP2 gene knockout mice, cellular models, and selective small molecule agonists and antagonists for this receptor. The efficacy data from in vitro and in vivo animal models indicate that EP2 receptor is a major proinflammatory mediator with deleterious functions in a variety of diseases suggesting a path forward for EP2 inhibitors as the next generation of selective anti-inflammatory and antiproliferative agents. Interestingly in certain diseases, EP2 action is beneficial; therefore, EP2 agonists seem to be clinically useful. Here, we highlight the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and potential threats (SWOT analysis) for targeting EP2 receptor for therapeutic development for a variety of unmet clinical needs.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares the following competing financial interest(s): T.G. is the inventor of the EP2 antagonists described in this Perspective and is the founder of and has equity in Pyrefin Inc., which has licensed EP2 technology from Emory University.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

