The histotripsy spectrum: differences and similarities in techniques and instrumentation
- PMID: 37460101
- PMCID: PMC10479943
- DOI: 10.1080/02656736.2023.2233720
The histotripsy spectrum: differences and similarities in techniques and instrumentation
Abstract
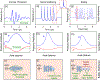
Since its inception about two decades ago, histotripsy - a non-thermal mechanical tissue ablation technique - has evolved into a spectrum of methods, each with distinct potentiating physical mechanisms: intrinsic threshold histotripsy, shock-scattering histotripsy, hybrid histotripsy, and boiling histotripsy. All methods utilize short, high-amplitude pulses of focused ultrasound delivered at a low duty cycle, and all involve excitation of violent bubble activity and acoustic streaming at the focus to fractionate tissue down to the subcellular level. The main differences are in pulse duration, which spans microseconds to milliseconds, and ultrasound waveform shape and corresponding peak acoustic pressures required to achieve the desired type of bubble activity. In addition, most types of histotripsy rely on the presence of high-amplitude shocks that develop in the pressure profile at the focus due to nonlinear propagation effects. Those requirements, in turn, dictate aspects of the instrument design, both in terms of driving electronics, transducer dimensions and intensity limitations at surface, shape (primarily, the F-number) and frequency. The combination of the optimized instrumentation and the bio-effects from bubble activity and streaming on different tissues, lead to target clinical applications for each histotripsy method. Here, the differences and similarities in the physical mechanisms and resulting bioeffects of each method are reviewed and tied to optimal instrumentation and clinical applications.
Keywords: High intensity focused ultrasound; boiling histotripsy; cavitation; histotripsy; nonlinear propagation.
Figures

References
-
- Parsons JE, Cain CA, Abrams GD, Fowlkes JB. Pulsed cavitational ultrasound therapy for controlled tissue homogenization. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2006;32(1):115–29. - PubMed
-
- Roberts W,W, Hall T,L, Ives K, Wolf JS, Fowlkes JB, Cain C,A Pulsed cavitational ultrasound: A noninvasive technology for controlled tissue ablation (histotripsy) in the rabbit kidney. J Urol. 2006;175(2):734–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
