Differential expression of IFN-α, IL-12 and BAFF on renal immune cells and its relevance to disease activity and treatment responsiveness in patients with proliferative lupus nephritis
- PMID: 37460249
- PMCID: PMC10357699
- DOI: 10.1136/lupus-2023-000962
Differential expression of IFN-α, IL-12 and BAFF on renal immune cells and its relevance to disease activity and treatment responsiveness in patients with proliferative lupus nephritis
Abstract
Objective: Since molecularly targeted therapies are emerging for treating lupus nephritis (LN), this study aimed to assess the immunohistochemical findings of the cytokines in renal tissue and their pathological and clinical relevance in LN.
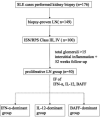
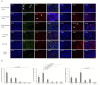
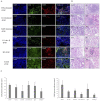
Methods: Fifty patients with proliferative LN formed the case group; 5 with LN class II, IgA nephropathy and 10 with idiopathic haematuria were enrolled as controls. Immunohistochemical analysis for CD3, CD20, interferon (IFN)-α, interleukin (IL)-12/p40 and B-cell activating factor (BAFF) was performed by scoring the number of positive cells/area of the cortex. All immunohistochemical investigations were performed on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded renal tissue. Proliferative LN cases were grouped by the dominant expression of IFN-α, IL-12/p40 and BAFF, and subsequently, clinicopathological features were compared.
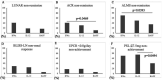
Results: Clinical data of patients with proliferative LN included urine protein creatinine ratio, 2.2 g/gCre; anti-double-stranded DNA antibody, 200.9 IU/mL; total complement activity (CH50), 21.9 U/mL and SLE Disease Activity Index, 19.8 points. Proliferative LN cases, including class III (n=18) and IV (n=32), were classified into three subgroups according to the immunohistochemical score based on the dominancy of IFN-α (n=17), IL-12 (n=16) and BAFF group (n=17) proteins. Hypocomplementaemia and glomerular endocapillary hypercellularity were significantly increased in the IFN-α group, whereas chronic lesions were significantly higher in the IL-12 group (p<0.05). The IFN-α group had a poorer renal prognosis in treatment response after 52 weeks.
Conclusions: The immunohistochemistry (IHC) of IFN-α, IL-12 and BAFF for proliferative LN enabled grouping. Especially, the IFN-α and IL-12 groups showed different clinicopathological features and renal prognoses. The results indicated the possibility of stratifying cases according to the IHC of target molecules, which might lead to precision medicine.
Keywords: cytokines; lupus erythematosus, systemic; lupus nephritis.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: SN has received consulting fees, speaking fees and/or honoraria from Bristol-Myers, AstraZeneca, Pfizer, GlaxoSmithKline, Astellas, Asahi-kasei, Sanofi, AbbVie, Eisai, Chugai, Gilead and Boehringer Ingelheim and has received research grants from Mitsubishi-Tanabe. YT has received speaking fees and/or honoraria from Behringer-Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, AbbVie, Gilead, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers, Chugai, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eisai, Pfizer, Mitsubishi-Tanabe and GlaxoSmithKline, and has received research grants from Asahi-Kasei, AbbVie, Chugai, Eisai, Takeda, Daiichi-Sankyo and Behringer-Ingelheim.
Figures
References
-
- Fanouriakis A, Kostopoulou M, Cheema K, et al. . Update of the joint European League against rheumatism and European renal Association-European dialysis and transplant Association (EULAR/ERA-EDTA) recommendations for the management of lupus nephritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79(Suppl 1):1028. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-eular.3936 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
