Mobilization-based engraftment of haematopoietic stem cells: a new perspective for chemotherapy-free gene therapy and transplantation
- PMID: 37460391
- PMCID: PMC10502445
- DOI: 10.1093/bmb/ldad017
Mobilization-based engraftment of haematopoietic stem cells: a new perspective for chemotherapy-free gene therapy and transplantation
Abstract
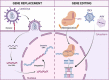
Introduction: In haematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) from a healthy donor replace the patient's ones. Ex vivo HSC gene therapy (HSC-GT) is a form of HSCT in which HSCs, usually from an autologous source, are genetically modified before infusion, to generate a progeny of gene-modified cells. In HSCT and HSC-GT, chemotherapy is administered before infusion to free space in the bone marrow (BM) niche, which is required for the engraftment of infused cells. Here, we review alternative chemotherapy-free approaches to niche voidance that could replace conventional regimens and alleviate the morbidity of the procedure.
Sources of data: Literature was reviewed from PubMed-listed peer-reviewed articles. No new data are presented in this article.
Areas of agreement: Chemotherapy exerts short and long-term toxicity to haematopoietic and non-haematopoietic organs. Whenever chemotherapy is solely used to allow engraftment of donor HSCs, rather than eliminating malignant cells, as in the case of HSC-GT for inborn genetic diseases, non-genotoxic approaches sparing off-target tissues are highly desirable.
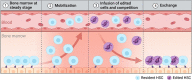
Areas of controversy: In principle, HSCs can be temporarily moved from the BM niches using mobilizing drugs or selectively cleared with targeted antibodies or immunotoxins to make space for the infused cells. However, translation of these principles into clinically relevant settings is only at the beginning, and whether therapeutically meaningful levels of chimerism can be safely established with these approaches remains to be determined.
Growing points: In pre-clinical models, mobilization of HSCs from the niche can be tailored to accommodate the exchange and engraftment of infused cells. Infused cells can be further endowed with a transient engraftment advantage.
Areas timely for developing research: Inter-individual efficiency and kinetics of HSC mobilization need to be carefully assessed. Investigations in large animal models of emerging non-genotoxic approaches will further strengthen the rationale and encourage application to the treatment of selected diseases.
Keywords: autologous stem cell transplantation; chemotherapy-free conditioning; gene therapy; haematopoietic stem and progenitor cells; mobilization.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
LN is the inventor of patents on applications of gene editing in HSPCs, and compositions and methods for haematopoietic stem cell transplantation, owned and managed by the San Raffaele Scientific Institute and the Telethon Foundation, including on improved gene editing filed together with by SF and DC, and increasing engraftment by HSPCs filed together with AO.
LN is the founder, quota holder and consultant of GeneSpire, a startup company developing gene therapies, including
Figures


References
-
- Galgano L, and Hutt D. Chapter 2 HSCT: How Does It Work? The European Blood and Marrow Transplantation Textbook for Nurses: Under the Auspices of EBMT. 2017. https://10.1007/978-3-319-50026-3_2. - DOI
-
- Spierings E, Fleischhauer K Histocompatibility. In: Carreras E, Dufour C, Mohty M, Kröger N (eds). The EBMT Handbook, 61–8 ( Springer International Publishing, 2019). doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-02278-5. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

