A renal YY1-KIM1-DR5 axis regulates the progression of acute kidney injury
- PMID: 37460623
- PMCID: PMC10352345
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-40036-z
A renal YY1-KIM1-DR5 axis regulates the progression of acute kidney injury
Abstract
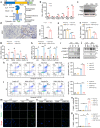
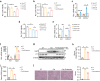
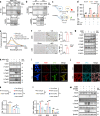
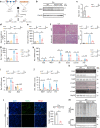
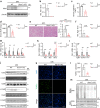
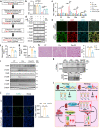
Acute kidney injury (AKI) exhibits high morbidity and mortality. Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM1) is dramatically upregulated in renal tubules upon injury, and acts as a biomarker for various renal diseases. However, the exact role and underlying mechanism of KIM1 in the progression of AKI remain elusive. Herein, we report that renal tubular specific knockout of Kim1 attenuates cisplatin- or ischemia/reperfusion-induced AKI in male mice. Mechanistically, transcription factor Yin Yang 1 (YY1), which is downregulated upon AKI, binds to the promoter of KIM1 and represses its expression. Injury-induced KIM1 binds to the ECD domain of death receptor 5 (DR5), which activates DR5 and the following caspase cascade by promoting its multimerization, thus induces renal cell apoptosis and exacerbates AKI. Blocking the KIM1-DR5 interaction with rationally designed peptides exhibit reno-protective effects against AKI. Here, we reveal a YY1-KIM1-DR5 axis in the progression of AKI, which warrants future exploration as therapeutic targets.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

