Experimental support for reclassification of the light scattering second virial coefficient from macromolecular solutions as a hydrodynamic parameter
- PMID: 37460663
- PMCID: PMC10444693
- DOI: 10.1007/s00249-023-01665-w
Experimental support for reclassification of the light scattering second virial coefficient from macromolecular solutions as a hydrodynamic parameter
Abstract
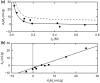
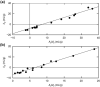
This investigation examines the source of the disparity between experimental values of the light scattering second virial coefficient [Formula: see text] (mL.mol/g2) for proteins and those predicted on the statistical mechanical basis of excluded volume. A much better theoretical description of published results for lysozyme is obtained by considering the experimental parameters to monitor the difference between the thermodynamic excluded volume term and its hydrodynamic counterpart. This involves a combination of parameters quantifying concentration dependence of the translational diffusion coefficient obtained from dynamic light scattering measurements. That finding is shown to account for observations of a strong correlation between [Formula: see text] (mL/g), where M2 is the molar mass (molecular weight) of the macromolecule and the diffusion concentration parameter [Formula: see text] (mL/g). On the grounds that [Formula: see text] is regarded as a hydrodynamic parameter, the same status should be accorded the light scattering second virial coefficient rather than its current incorrect thermodynamic designation as [Formula: see text] (mL.mol/g2), or just B, the osmotic second virial coefficient for protein self-interaction.
Keywords: Dynamic light scattering; Hydrodynamics; Lysozyme; Monoclonal IgG antibodies; Second virial coefficient; Static light scattering; Statistical mechanics; Thermodynamic nonideality.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Batchelor GK. Brownian diffusion of particles with hydrodynamic interaction. J Fluid Mech. 1976;74:1–29.
-
- Behlke J, Ristau O. Analysis of the thermodynamic nonideality of proteins by sedimentation equilibrium experiments. Biophys Chem. 1999;76:13–23. - PubMed
-
- Brady JF, Durlofsky J. The sedimentation rate of disordered suspensions. J Phys Fluids. 1988;31:717–727.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

