Dissecting peri-implantation development using cultured human embryos and embryo-like assembloids
- PMID: 37460804
- PMCID: PMC10474050
- DOI: 10.1038/s41422-023-00846-8
Dissecting peri-implantation development using cultured human embryos and embryo-like assembloids
Abstract
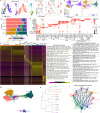
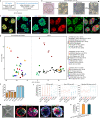
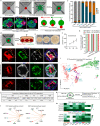
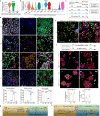
Studies of cultured embryos have provided insights into human peri-implantation development. However, detailed knowledge of peri-implantation lineage development as well as underlying mechanisms remains obscure. Using 3D-cultured human embryos, herein we report a complete cell atlas of the early post-implantation lineages and decipher cellular composition and gene signatures of the epiblast and hypoblast derivatives. In addition, we develop an embryo-like assembloid (E-assembloid) by assembling naive hESCs and extraembryonic cells. Using human embryos and E-assembloids, we reveal that WNT, BMP and Nodal signaling pathways synergistically, but functionally differently, orchestrate human peri-implantation lineage development. Specially, we dissect mechanisms underlying extraembryonic mesoderm and extraembryonic endoderm specifications. Finally, an improved E-assembloid is developed to recapitulate the epiblast and hypoblast development and tissue architectures in the pre-gastrulation human embryo. Our findings provide insights into human peri-implantation development, and the E-assembloid offers a useful model to disentangle cellular behaviors and signaling interactions that drive human embryogenesis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
Studying human embryo development with E-assembloids.Cell Res. 2023 Oct;33(10):737-738. doi: 10.1038/s41422-023-00863-7. Cell Res. 2023. PMID: 37563444 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

