Mannose antagonizes GSDME-mediated pyroptosis through AMPK activated by metabolite GlcNAc-6P
- PMID: 37460805
- PMCID: PMC10709431
- DOI: 10.1038/s41422-023-00848-6
Mannose antagonizes GSDME-mediated pyroptosis through AMPK activated by metabolite GlcNAc-6P
Abstract
Pyroptosis is a type of regulated cell death executed by gasdermin family members. However, how gasdermin-mediated pyroptosis is negatively regulated remains unclear. Here, we demonstrate that mannose, a hexose, inhibits GSDME-mediated pyroptosis by activating AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). Mechanistically, mannose metabolism in the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway increases levels of the metabolite N-acetylglucosamine-6-phosphate (GlcNAc-6P), which binds AMPK to facilitate AMPK phosphorylation by LKB1. Activated AMPK then phosphorylates GSDME at Thr6, which leads to blockade of caspase-3-induced GSDME cleavage, thereby repressing pyroptosis. The regulatory role of AMPK-mediated GSDME phosphorylation was further confirmed in AMPK knockout and GSDMET6E or GSDMET6A knock-in mice. In mouse primary cancer models, mannose administration suppressed pyroptosis in small intestine and kidney to alleviate cisplatin- or oxaliplatin-induced tissue toxicity without impairing antitumor effects. The protective effect of mannose was also verified in a small group of patients with gastrointestinal cancer who received normal chemotherapy. Our study reveals a novel mechanism whereby mannose antagonizes GSDME-mediated pyroptosis through GlcNAc-6P-mediated activation of AMPK, and suggests the utility of mannose supplementation in alleviating chemotherapy-induced side effects in clinic applications.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


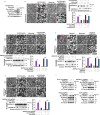

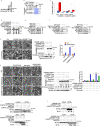



References
-
- Treebak JT, Birk JB, Hansen BF, Olsen GS, Wojtaszewski JF. A-769662 activates AMPK beta1-containing complexes but induces glucose uptake through a PI3-kinase-dependent pathway in mouse skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2009;297:C1041–C1052. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00051.2009. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

