Neuromodulatory effect of vardenafil on aluminium chloride/D-galactose induced Alzheimer's disease in rats: emphasis on amyloid-beta, p-tau, PI3K/Akt/p53 pathway, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and cellular senescence
- PMID: 37460908
- PMCID: PMC10518298
- DOI: 10.1007/s10787-023-01287-w
Neuromodulatory effect of vardenafil on aluminium chloride/D-galactose induced Alzheimer's disease in rats: emphasis on amyloid-beta, p-tau, PI3K/Akt/p53 pathway, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and cellular senescence
Abstract
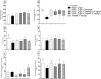
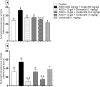
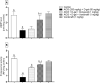
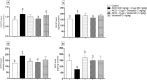
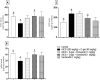
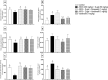
Dysregulation of protein homeostasis, proteostasis, is a distinctive hallmark of many neurodegenerative disorders and aging. Deleteriously, the accumulation of aberrant proteins in Alzheimer's disease (AD) is accompanied with a marked collapse in proteostasis network. The current study explored the potential therapeutic effect of vardenafil (VAR), a phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor, in AlCl3/D-galactose (D-gal)-induced AD in rats and its possible underlying mechanisms. The impact of VAR treatment on neurobehavioral function, hippocampal tissue architecture, and the activity of the cholinergic system main enzymes were assessed utilizing VAR at doses of 0.3 mg/kg and 1 mg/kg. Additionally, the expression level of amyloid-beta and phosphorylated tau proteins in the hippocampus were figured out. Accordingly, VAR higher dose was selected to contemplate the possible underlying mechanisms. Intriguingly, VAR elevated the cyclic guanosine monophosphate level in the hippocampus and averted the repressed proteasome activity by AlCl3/D-gal; hence, VAR might alleviate the burden of toxic protein aggregates in AD. In addition, a substantial reduction in the activating transcription factor 6-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress was demonstrated with VAR treatment. Notably, VAR counteracted the AlCl3/D-gal-induced depletion of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 level. Moreover, the anti-senescence activity of VAR was demonstrated via its ability to restore the balance of the redox circuit. The modulation of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/protein kinase B/p53 pathway and the reduction of nuclear factor kappa B level, the key regulator of senescence-associated secretory phenotype mediators release, with VAR treatment were also elucidated. Altogether, these findings insinuate the possible therapeutic benefits of VAR in AD management.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s; Endoplasmic reticulum stress; PI3K/Akt/p53; Proteasome activation; Senescence; Vardenafil.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective effects of ginseng protein on PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in the hippocampus of D-galactose/AlCl3 inducing rats model of Alzheimer's disease.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Feb 17;179:162-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.12.020. Epub 2015 Dec 23. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26721223
-
Stimulation of ACE2/ANG(1-7)/Mas Axis by Diminazene Ameliorates Alzheimer's Disease in the D-Galactose-Ovariectomized Rat Model: Role of PI3K/Akt Pathway.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Oct;55(10):8188-8202. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-0966-3. Epub 2018 Mar 7. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 29516284
-
Neuroprotective effects of vitamin D in an Alzheimer's disease rat model: Improvement of mitochondrial dysfunction via calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2 activation of Sirtuin1 phosphorylation.Biofactors. 2024 Mar-Apr;50(2):371-391. doi: 10.1002/biof.2013. Epub 2023 Oct 6. Biofactors. 2024. PMID: 37801071
-
Proteostasis disruption and senescence in Alzheimer's disease pathways to neurodegeneration.Brain Res. 2024 Dec 15;1845:149202. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2024.149202. Epub 2024 Aug 30. Brain Res. 2024. PMID: 39216694 Review.
-
Redox changes and cellular senescence in Alzheimer's disease.Redox Biol. 2024 Apr;70:103048. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103048. Epub 2024 Jan 17. Redox Biol. 2024. PMID: 38277964 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Promoting proteostasis by cAMP/PKA and cGMP/PKG.Trends Mol Med. 2025 Mar;31(3):224-239. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2024.10.006. Epub 2024 Oct 29. Trends Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 39477759 Review.
-
Empagliflozin Alleviates Carfilzomib-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Mice by Modulating Oxidative Stress, Inflammatory Response, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Autophagy.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 May 30;13(6):671. doi: 10.3390/antiox13060671. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38929110 Free PMC article.
-
Polypharmacological Potential of Phosphodiesterase 5 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Neurocognitive Disorders.Aging Dis. 2024 Oct 1;15(5):2008-2014. doi: 10.14336/AD.2023.1129. Aging Dis. 2024. PMID: 38270120 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression and potential regulatory mechanism of cellular senescence-related genes in Alzheimer's disease based on single-cell and bulk RNA datasets.Front Neurosci. 2025 May 21;19:1595847. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1595847. eCollection 2025. Front Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40470298 Free PMC article.
-
Ameliorative Role of Phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE-5) Inhibitor "Avanafil" via Modulating cAMP & cGMP Pathway Against Alzheimer's Disease.Neurochem Res. 2025 Aug 13;50(4):258. doi: 10.1007/s11064-025-04516-6. Neurochem Res. 2025. PMID: 40802200
References
-
- Ahmad Rather M, Justin-Thenmozhi A, Manivasagam T, Saravanababu C, Guillemin GJ, Essa MM. Asiatic acid attenuated aluminum chloride-induced tau pathology, oxidative stress and apoptosis via AKT/GSK-3β signaling pathway in wistar rats. Neurotox Res. 2019;35(4):955–968. doi: 10.1007/s12640-019-9999-2. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
