Novel cancer treatment paradigm targeting hypoxia-induced factor in conjunction with current therapies to overcome resistance
- PMID: 37460927
- PMCID: PMC10353250
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-023-02724-y
Novel cancer treatment paradigm targeting hypoxia-induced factor in conjunction with current therapies to overcome resistance
Abstract
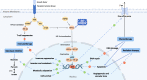
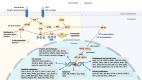
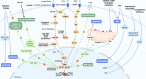
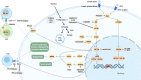
Chemotherapy, radiotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy are established cancer treatment modalities that are widely used due to their demonstrated efficacy against tumors and favorable safety profiles or tolerability. Nevertheless, treatment resistance continues to be one of the most pressing unsolved conundrums in cancer treatment. Hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) are a family of transcription factors that regulate cellular responses to hypoxia by activating genes involved in various adaptations, including erythropoiesis, glucose metabolism, angiogenesis, cell proliferation, and apoptosis. Despite this critical function, overexpression of HIFs has been observed in numerous cancers, leading to resistance to therapy and disease progression. In recent years, much effort has been poured into developing innovative cancer treatments that target the HIF pathway. Combining HIF inhibitors with current cancer therapies to increase anti-tumor activity and diminish treatment resistance is one strategy for combating therapeutic resistance. This review focuses on how HIF inhibitors could be applied in conjunction with current cancer treatments, including those now being evaluated in clinical trials, to usher in a new era of cancer therapy.
Keywords: Chemotherapy; Combination therapy; HIF-1; HIF-2; Hypoxia; Immunotherapy; Metabolic therapy; Radiotherapy; Target therapy; Therapeutic resistance.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no potential conflicts of interest concerning the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

