Biomechanical analysis of different osteosynthesis configurations in the pin and plate fixation method for distal humerus fractures
- PMID: 37460939
- PMCID: PMC10351186
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-023-06709-y
Biomechanical analysis of different osteosynthesis configurations in the pin and plate fixation method for distal humerus fractures
Abstract
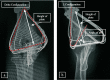
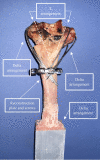
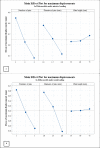
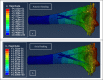
Distal humerus fractures commonly occur in adults with low bone mineral density causing major technical challenges for orthopedic surgeons. Persian fixation method was introduced as a novel technique to stabilize small fragments in comminuted distal humerus fractures using a set of K-wires and a reconstruction plate. The present study aims to measure this technique's stiffness and stability of this technique and analyze the effect of influential parameters with numerical simulation and biomechanical testing on a cadaveric specimen. Validation of the finite element (FE) model was conducted based on results of experiments. The results indicated that Delta configuration mainly led to a higher stiffness in the case of axial loading and anterior bending compared to L configuration. Analyzing the influential factors of this technique suggests that changes in diameter and number of K-wires have a similarly significant effect on the construct stiffness while the height of plate had a slight influence. Also, the diameter of wires was the most effective parameter for implant failure, particularly in the 3-pin construct, which caused a reduction in failure risk by about 60%. The results revealed that the Persian fixation method would achieve suitable stability compared to the dual-plating technique.
Keywords: Biomechanical testing; Distal humerus fracture; Osteosynthesis; Persian fixation method; Stability.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Cadaveric biomechanical assessment of different configurations for a novel pin and plate fixation method in distal humerus fractures.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 2;14(1):242. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-50976-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38168602 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative study of three models of extra-articular distal humerus fracture osteosynthesis using the finite element method on an osteoporotic computational model.Injury. 2013 Sep;44 Suppl 3:S56-61. doi: 10.1016/S0020-1383(13)70200-6. Injury. 2013. PMID: 24060021
-
A novel configuration for the fixation of intra-articular C2.3 distal humerus fractures with the potential for minimally invasive surgery: a biomechanical evaluation and finite element analysis.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2024 May;33(5):1138-1149. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2023.09.034. Epub 2023 Nov 7. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2024. PMID: 37944743
-
Parallel versus orthogonal plate osteosynthesis of adult distal humerus fractures: a meta-analysis of biomechanical studies.Int Orthop. 2019 Feb;43(2):449-460. doi: 10.1007/s00264-018-3937-4. Epub 2018 Apr 20. Int Orthop. 2019. PMID: 29679109
-
Biomechanical Design Optimization of Distal Humerus Fracture Plates: A Review.Biomed Res Int. 2024 Jun 27;2024:6015794. doi: 10.1155/2024/6015794. eCollection 2024. Biomed Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38966093 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cadaveric biomechanical assessment of different configurations for a novel pin and plate fixation method in distal humerus fractures.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 2;14(1):242. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-50976-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38168602 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Srinivasan K, Agarwal M, Matthews SJE, Giannoudis PV. Fractures of the Distal Humerus in the Elderly. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. 2005;(434):222–30. 10.1097/01.blo.0000154010.43568.5b. - PubMed
-
- Korner J, Diederichs G, Arzdorf M, Lill H, Josten C, Schneider E, Linke B. A biomechanical evaluation of methods of distal humerus fracture fixation using locking compression plates versus conventional reconstruction plates. J Orthop Trauma. 2004;18(5):286–293. doi: 10.1097/00005131-200405000-00004. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

