Semi-automated quantification of vitreal hyperreflective foci in SD-OCT and their relevance in patients with peripheral retinal breaks
- PMID: 37460946
- PMCID: PMC10353228
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-023-03060-7
Semi-automated quantification of vitreal hyperreflective foci in SD-OCT and their relevance in patients with peripheral retinal breaks
Abstract
Background: Retinal breaks (RB) are emergencies that require treatment to prevent progression of rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. Vitreal hyperreflective foci (VHF) representing migration of RPE cell clusters or interphotoreceptor matrix from the RB are potential biomarkers. The aim of this study is to investigate VHF in RB-patients using SD-OCT.
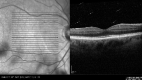
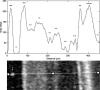
Methods: The retrospective cross-sectional study included RB patients from our Department of Ophthalmology, HSK Wiesbaden who underwent macular SD-OCT (SPECTRALIS®, Heidelberg Engineering, Germany) on both eyes. VHF, defined and quantified as foci that differ markedly in size and reflectivity from the background speckle pattern, were assessed for presence and frequency. The RB-affected eyes were the study group (G1), the partner eyes the control group (G2).
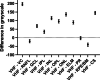
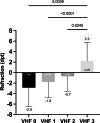
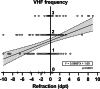
Results: 160 consecutive patients with RB were included. Age was 60 ± 10.2 years (52% female). 89.4% of G1 and 87.5% of G2 were phakic (p = 0.73). 94.4% (n = 151) were symptomatic. Symptom duration was 8.0 ± 10.1 days in G1, 94.4% (n = 151) showed VHF versus 5.6% (p < 0.0001) in G2, of which 75% (n = 6) showed asymptomatic lattice degenerations. Detectable VHF showed a strong association of OR = 320 (95% CI, 110-788, p < 0.0001)) with respect to symptomatic RB. Sensitivity and specificity were 94.7% and 94.7%, respectively.
Conclusions: Most eyes with symptomatic RB show vitreal VHF in SD-OCT. Detected VHF are strongly associated with RB, and our semi-automated greyscale reflectivity analysis indicates that VHF likely originate from photoreceptor complexes torn out of the RB area that migrate into the vitreous cavity. The presence of VHF may indicate RB and should lead to a thorough fundus examination in both symptomatic and asymptomatic cases.
Keywords: OCT biomarker; Retinal break; SD-OCT; Semi-automated quantification; Vitreal hyperreflective foci; Vitreoretinal disorders.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Chen X, Xiao W, Wang W, Luo L, Ye S, Liu Y. The complex interplay between ERK1/2, TGFβ/Smad, and Jagged/Notch signaling pathways in the regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in retinal pigment epithelium cells. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e96365. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096365. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

