Direct comparison of diagnostic and clinical values between Tc-99 m DPD and Tc-99 m PYP scintigraphy in patients with cardiac amyloidosis
- PMID: 37460984
- PMCID: PMC10353145
- DOI: 10.1186/s12880-023-01054-x
Direct comparison of diagnostic and clinical values between Tc-99 m DPD and Tc-99 m PYP scintigraphy in patients with cardiac amyloidosis
Abstract
Background: Technetium-99 m 3,3-diphosphono-1,2-propanodicarboxylic acid (DPD) and technetium-99 m sodium pyrophosphate (PYP) are the two most commonly used radiotracers for cardiac amyloidosis (CA), but no studies have directly compared them. Therefore, in this study, we directly compared the diagnostic and clinical utility of DPD and PYP scintigraphy in patients with CA.
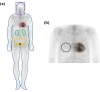
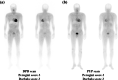
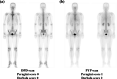
Methods: Ten patients with CA were enrolled. Eight clinical variables and 12 scintigraphic parameters were used. Clinical variables were age, sex, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), N-terminal pro brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), and the results of electromyography (EMG), a sensory test, electrocardiogram, and echocardiography (EchoCG). Four heart retention ratios (heart/whole-body profile, heart/pelvis, heart/skull, and heart/contralateral lung) were calculated from the DPD and PYP scans and two visual scoring systems (Perugini and Dorbala systems) were used. Comparative analyses were performed between radiotracers and between visual scoring systems using clinical variables and scintigraphic parameters.
Results: Twenty DPD parameters and nine PYP parameters had significant associations with age, eGFR, NT-proBNP, EchoCG, and EMG. DPD parameters had more frequent significant associations with clinical variables than PYP parameters. Compared to visual scores in the DPD scan, the proportion of patients with higher visual scores in the PYP scan was relatively greater than those with lower visual scores, and there were more patients with a visual score of 2 or higher in PYP scans than DPD scans.
Conclusions: DPD scintigraphy may reflect the disease severity of CA better than PYP scintigraphy, whereas PYP scintigraphy may be a more sensitive imaging modality for identifying CA involvement.
Keywords: Cardiac amyloidosis; Dorbala system; Perugini system; Tc-99m DPD; Tc-99m PYP.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hotta VT, Giorgi MCP, Fernandes F, Abduch MCD, Falcão A, Mady C. Cardiac amyloidosis: non-invasive diagnosis. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992) 2020, 66(3):345–352. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

