Machine learning applications for early detection of esophageal cancer: a systematic review
- PMID: 37460991
- PMCID: PMC10351192
- DOI: 10.1186/s12911-023-02235-y
Machine learning applications for early detection of esophageal cancer: a systematic review
Abstract
Introduction: Esophageal cancer (EC) is a significant global health problem, with an estimated 7th highest incidence and 6th highest mortality rate. Timely diagnosis and treatment are critical for improving patients' outcomes, as over 40% of patients with EC are diagnosed after metastasis. Recent advances in machine learning (ML) techniques, particularly in computer vision, have demonstrated promising applications in medical image processing, assisting clinicians in making more accurate and faster diagnostic decisions. Given the significance of early detection of EC, this systematic review aims to summarize and discuss the current state of research on ML-based methods for the early detection of EC.
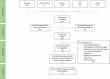
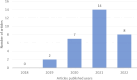
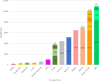
Methods: We conducted a comprehensive systematic search of five databases (PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, Wiley, and IEEE) using search terms such as "ML", "Deep Learning (DL (", "Neural Networks (NN)", "Esophagus", "EC" and "Early Detection". After applying inclusion and exclusion criteria, 31 articles were retained for full review.
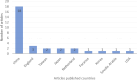
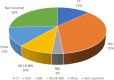
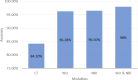
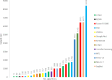
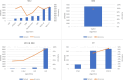
Results: The results of this review highlight the potential of ML-based methods in the early detection of EC. The average accuracy of the reviewed methods in the analysis of endoscopic and computed tomography (CT (images of the esophagus was over 89%, indicating a high impact on early detection of EC. Additionally, the highest percentage of clinical images used in the early detection of EC with the use of ML was related to white light imaging (WLI) images. Among all ML techniques, methods based on convolutional neural networks (CNN) achieved higher accuracy and sensitivity in the early detection of EC compared to other methods.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that ML methods may improve accuracy in the early detection of EC, potentially supporting radiologists, endoscopists, and pathologists in diagnosis and treatment planning. However, the current literature is limited, and more studies are needed to investigate the clinical applications of these methods in early detection of EC. Furthermore, many studies suffer from class imbalance and biases, highlighting the need for validation of detection algorithms across organizations in longitudinal studies.
Keywords: Deep learning; Early detection; Esophageal Cancer; Esophagus; Machine learning.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests
Figures
References
-
- National Cancer Institute Esophageal Cancer. 2021 [Available from: https://www.cancer.gov/types/esophageal.
-
- Yamanouchi S, Sako Y, Suemitsu S, Tsukano K, Kotani S, Kusunoki R, et al. Early esophageal cancer with epidermization diagnosed and treated with endoscopic resection. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2018;11:29–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

